The ability of modern computers to enter sleep mode, conserving energy while enabling quick resumption of work, is highly beneficial. However, periodically restarting your computer is essential for applying updates and ensuring optimal performance. This guide will demonstrate various methods to safely restart your computer, emphasizing the importance of avoiding improper shutdowns that could lead to data loss.
Safely restarting your computer means avoiding methods that can cause harm, such as holding down the power button or unplugging the device, which can lead to data corruption or loss. Instead, follow the steps below to restart your Windows 11 or Windows 10 computer using safe and recommended methods.
How to Restart Your Computer from the Start Menu
The most popular way to restart a Windows computer is from the power button on the Start menu. This is quick, easy, and safe:
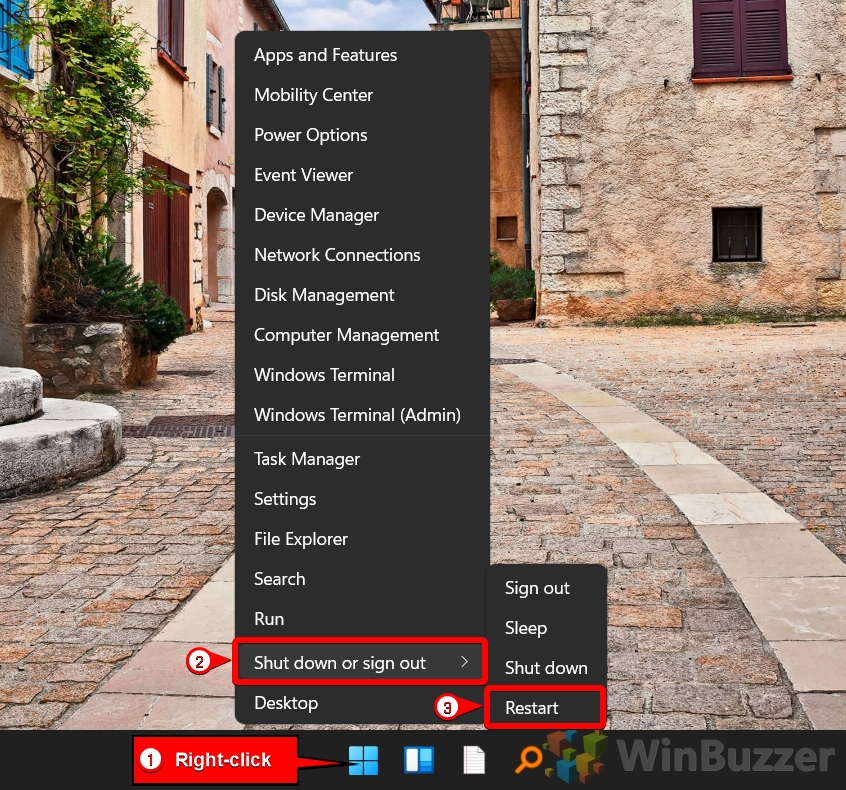
How to Reboot and Computer with the Power User Menu
Alternatively, you can access the power menu with a quick right-click on the Start icon:
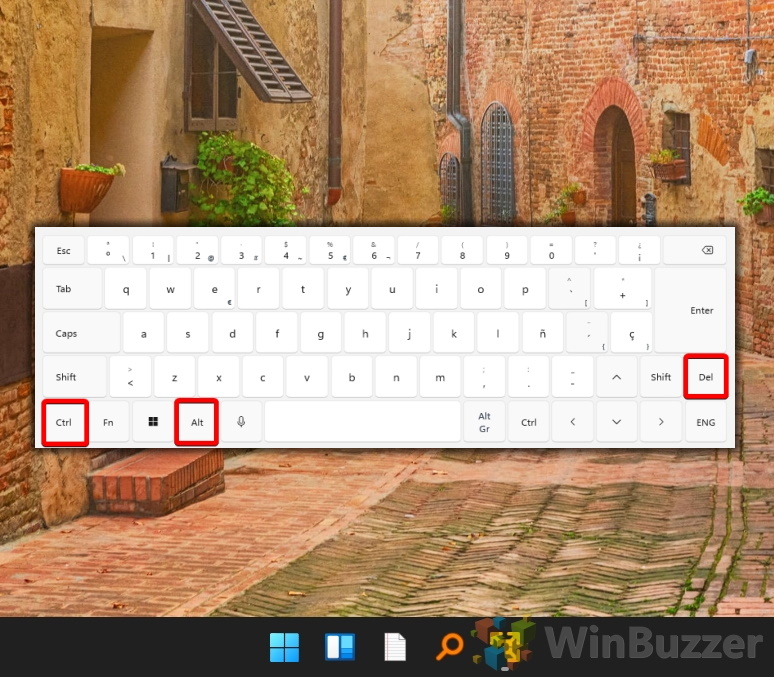
How to Restart Your Computer with the Ctrl+Alt+Del Menu
If you can’t easily access the Start menu because it has crashed or you’re in a fullscreen application, you can use the Ctrl + Alt + Del menu instead:
How to Use a Command to Restart a Computer
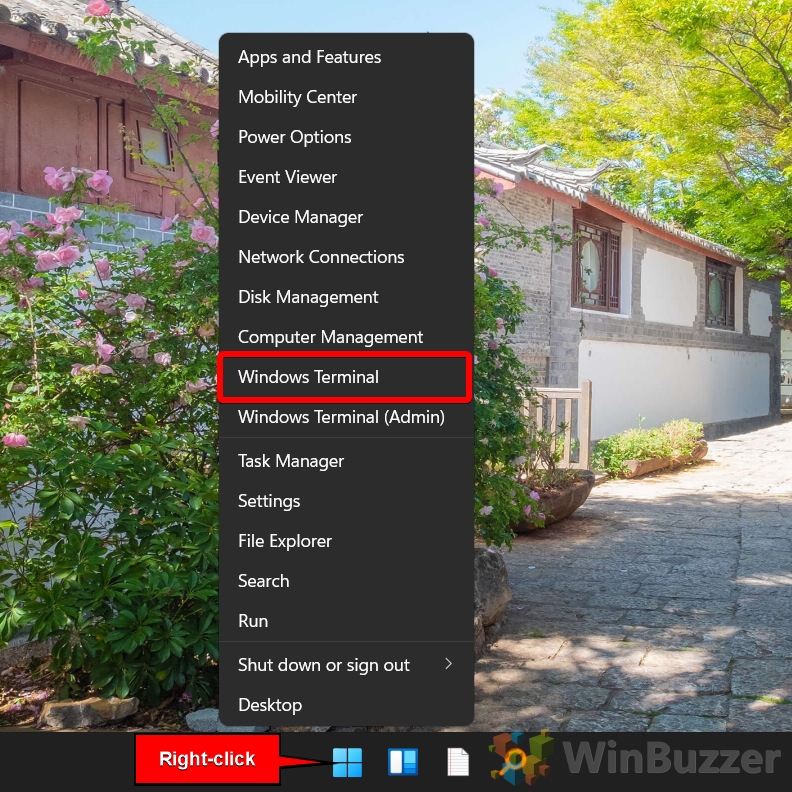
If none of the above options are working or you’re using a server install without a GUI, you can restart Windows with CMD (Command Prompt). In Windows 11, we’ll be accessing CMD through the Windows Terminal.
- Open Windows Terminal
Access the Windows Terminal by right-clicking the Start menu. On Windows 10, you can directly open the Command Prompt instead.

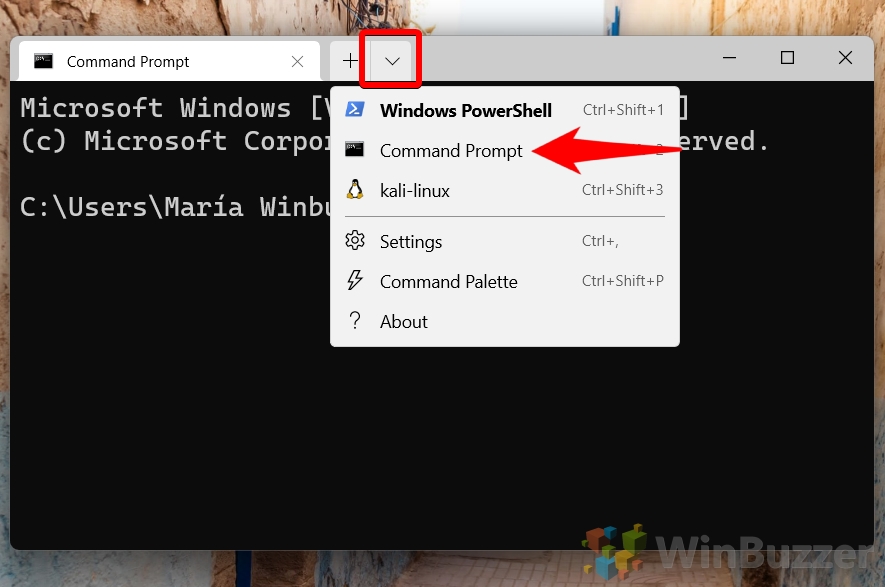
- Select Command Prompt (Windows Terminal)
In the Windows Terminal, click the dropdown next to the new tab button and select “Command Prompt”.

- Enter the Shutdown Command
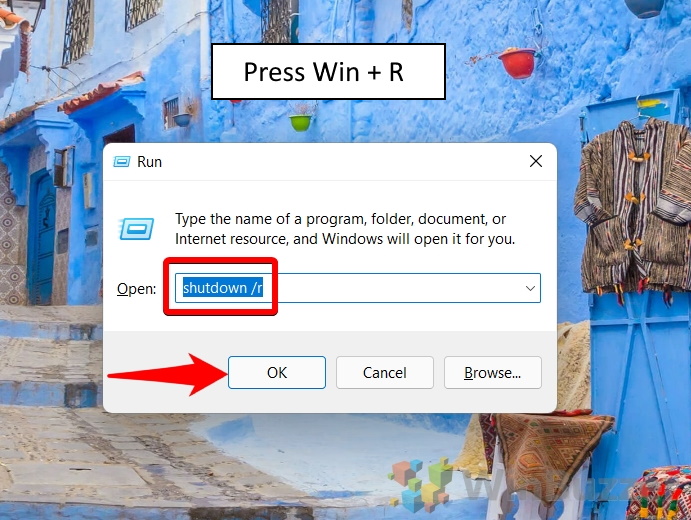
Type “shutdown /r” and press Enter to command your PC to restart immediately.

How to Reboot a Computer from the Run Dialog
Interestingly, you don’t have to open Command Prompt to run a restart command on Windows. You can instead type the command to restart your computer directly in the Run dialog, like so:
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Restarting Windows PCs
Is it better to shut down or restart my computer for performance?
Choosing between shutting down and restarting your computer depends on your needs. Restarting is beneficial for performance as it clears temporary files, flushes RAM, and applies any pending updates, which can enhance system efficiency. Shutting down, on the other hand, is more about conserving energy and giving your hardware a rest, especially if you won’t be using the computer for an extended period. For daily use, restarting can help resolve minor glitches and ensure your system runs smoothly.
How often should I reboot my computer to maintain optimal performance?
Regular reboots can help maintain your computer’s performance by clearing memory leaks and ensuring updates are applied. A good rule of thumb is to restart your computer at least once a week. However, if you frequently install new applications, receive updates, or experience performance issues, more frequent restarts might be beneficial. Pay attention to your computer’s performance and stability to determine the best reboot frequency for your specific usage patterns.
Can I create a restart shortcut in Windows 11?
Yes, creating a restart shortcut in Windows 11 is a convenient way to reboot your system with just a few clicks. Use the same method like for a shutdown shortcut, and in the location field, type shutdown /r /t 0. This command tells your computer to restart immediately (/r) without any delay (/t 0). Name the shortcut as you wish, for example, “Restart Now“. You can also change the icon to make it easily recognizable. This shortcut can be particularly useful for users who prefer quick access to system commands or those with specific accessibility needs.
What is the difference between rebooting and resetting a computer?
Rebooting, or restarting, your computer involves turning it off and then back on again, which can help resolve minor software issues and apply updates. Resetting, however, is a more drastic action that restores your computer to its original state, often as it was when you first purchased it. This process can involve reinstalling the operating system and may result in the loss of personal data and installed applications. Resetting is typically used as a last resort to resolve significant system issues or to prepare a device for a new user.
How do I boot into Safe Mode in Windows 11?
Booting into Safe Mode in Windows 11 can be crucial for troubleshooting issues. To enter Safe Mode, restart your computer and press the F8 key repeatedly as it boots up. This should bring up the Advanced Boot Options menu. If F8 doesn’t work due to fast boot times, you can also access Safe Mode through the system settings. Navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery, under Advanced startup, click “Restart now”. Once your computer reboots to the Choose an Option screen, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and then click “Restart”. After your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of options; select 4 or F4 to start your PC in Safe Mode.
What does Alt + F4 do?
Pressing Alt + F4 is a quick keyboard shortcut that closes the currently active window or application. If no applications are open, using Alt + F4 will bring up the shutdown dialog, allowing you to shut down, restart, or put your computer to sleep. This shortcut is particularly useful for quickly exiting programs or when a mouse is not functioning properly. However, it’s important to save any open work before using Alt + F4 to avoid losing unsaved data.
How do I restart my computer in repair mode?
Restarting your computer in repair mode, also known as Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE), can help fix common startup problems. To access repair mode, you’ll need to initiate a restart and then enter the boot options menu, usually by pressing F8 or Shift + F8 as the computer starts up. If this doesn’t work due to fast startup times, you can also access WinRE from within Windows by navigating to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery, and under Advanced startup, click “Restart now”. Once in WinRE, you can use various tools like “Startup Repair” to diagnose and fix issues.
What is a hard reboot, and how do I perform it?
A hard reboot, also known as a hard reset, involves forcibly shutting down and restarting your computer, typically by holding down the power button for about 10 seconds until the computer turns off, then pressing it again to turn it back on. This method should be used sparingly, as it bypasses the normal shutdown process and can lead to data loss or corruption, especially if programs are running or files are open. It’s most often used when the computer is completely unresponsive, and other restart methods are not working.
Is it safe to force restart my PC if it’s unresponsive?
Force restarting your PC should be considered a last resort, especially if the system is unresponsive due to software freezes or other issues. While it can help regain control of your computer, it bypasses the normal shutdown process, potentially leading to unsaved data loss or, in rare cases, system file corruption. Before force restarting, try other methods like the “Ctrl + Alt + Del” menu to see if you can gracefully shut down programs or log out. If these methods fail and your system remains unresponsive, a force restart may be necessary.
Will I lose my Windows 11 license if I reset my PC?
Resetting your PC in Windows 11 should not affect your Windows license. Windows activation is typically tied to your device’s hardware or a digital license linked to your Microsoft account, allowing you to reset or reinstall Windows without losing activation. However, it’s always a good idea to ensure you have your product key or digital entitlement information handy, just in case you need to manually reactivate Windows after a system reset.
How do I fix my computer if it’s stuck on a black screen?
If your computer is stuck on a black screen, it could be due to various issues, from simple software glitches to hardware problems. Start by checking if the computer is truly unresponsive by pressing the Caps Lock key and seeing if the indicator light changes. If the system seems alive, try a soft reset by pressing “Ctrl + Alt + Del” to see if you can bring up the security options screen. If this doesn’t work, a hard reboot might be necessary. For recurring black screen issues, booting into Safe Mode or using Windows Recovery Environment can help diagnose and fix the underlying problem.
How do I enable fast startup in Windows 11?
Fast startup in Windows 11 is a feature that helps your PC start up faster after a shutdown by saving the system state to a hibernation file. To enable it, go to Control Panel > System and Security > Power Options, and click on “Choose what the power buttons do”. Then click on “Change settings that are currently unavailable” and check the box for “Turn on fast startup (recommended)”. Note that while fast startup can significantly reduce boot times, it may also cause issues with dual-boot systems or when accessing BIOS settings.
Is it bad to restart my PC multiple times a day?
Restarting your PC multiple times a day is generally not harmful, but it’s usually unnecessary unless you’re troubleshooting, applying updates, or experiencing performance issues. Frequent restarts can be time-consuming and may interrupt your workflow. If you find yourself needing to restart often, it might be worth investigating the underlying cause, such as software conflicts or memory leaks, to address the root of the issue.
How do I clean restart Windows 11?
Performing a clean restart in Windows 11, also known as a clean boot, can help diagnose and troubleshoot software conflicts. To do this, type “msconfig” in the Start menu search and select “System Configuration”. In the Services tab, check “Hide all Microsoft services” and then click “Disable all” to turn off third-party services. Next, go to the Startup tab and open Task Manager to disable all startup items. After applying these changes, restart your computer. This state will start Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs, making it easier to identify the cause of any issues.
What happens if I never restart my PC?
Failing to restart your PC regularly can lead to decreased performance over time. The system may become sluggish due to the accumulation of temporary files, memory leaks, and unresolved minor software glitches. Regular restarts clear the system’s memory, apply updates, and refresh the operating system, which can help maintain or improve performance. If you’re experiencing performance issues, a restart is often the first troubleshooting step recommended.
Related: Windows Startup Problems? Use Startup Repair to Fix Your Boot
When Windows runs into serious problems, it’s not rare to run into startup problems. Corrupted Windows files, incorrect system configuration, driver failure, or registry tweaks can all cause this issue. Thankfully, this common problem has a common solution – the Windows startup repair tool. In our other guide, we show you how to use the Windows Startup repair tool to fix your boot when you can’t get into the main OS.

Related: How to Create a Windows 11 Shutdown Shortcut
One final way to restart your PC is through a Windows 11 shutdown shortcut. You can then single-click an icon on your taskbar or double-click a desktop shortcut to restart your PC. For that, though, you’ll have to follow our dedicated Windows 11 shutdown shortcut tutorial.
![]()
Related: How to Auto Shutdown and Auto Restart Windows
Finally, if manually restarting your PC is still too much for you, you can set your PC to restart automatically at a certain time. Just follow our Windows 10 shutdown tutorial and add /r in the arguments box instead of /s.
Related: How to Enable or Disable Login after Sleep/Standby
Windows’s uniformity across devices is essential for usability, but it can also cause problems when updates change things. On some versions of the OS, Windows disables login after sleep. On others, it needs a password, leading to confusion. In our other guide, we show you how to enable or disable the log-in screen after your Windows PC goes to sleep, both on battery and wall power.

Last Updated on April 22, 2024 10:30 am CEST by Markus Kasanmascheff