The graphics driver is a software component that communicates with the graphics hardware and Windows to render images on the screen. When you restart a graphics driver in Windows, you reset the graphics hardware’s state and force Windows 11/Windows 10 to reload the driver software. This can be done while your system is running without any reboot or logging off and might fix temporary glitches, performance problems, or compatibility errors of the graphics chipset.
The Difference of Dedicated GPU vs. Integrated Graphics
A GPU (graphics processing unit) is a specialized chip that handles the processing of graphics-related data and instructions. A GPU can be either integrated or dedicated. An integrated GPU is built into the same microchip package as the CPU (central processing unit) and shares the same system memory. A dedicated GPU has its own separate processor package, RAM (random access memory), cooling and circuit board. Dedicated GPUs typically offer better performance and more features than integrated GPUs but consume more power and generate more heat.
As modern Intel CPUs already include an integrated graphics processor, systems with a dedicated GPU will have both drivers for the integrated Intel hardware and the GPU.
What Happens When You Restart a Graphics Driver in Windows
Restarting a graphics driver in Windows involves sending a special signal to the graphics hardware, which causes it to stop processing any commands and release any resources it is currently using. Then, Windows unloads the driver software from memory and reloads it again. Finally, Windows sends another signal to the graphics hardware to resume its normal operation.
Reset the Graphics Driver to Fix Driver Issues in Windows
You can uninstall a graphics driver in Windows 11/Windows 10 to reset it to its original version. Depending on how you uninstall the driver, different things may happen. Windows 11/Windows 10 will then try to reinstall it automatically as soon as it detects the device.
Update the Graphics Driver in Windows 11 or Windows 10
With some exceptions due to compatibility issues or bugs, you should always strive to update the graphics driver in Windows 11/Windows 10 for the following benefits:
– Improving the performance and stability of your graphics card and applications that use it. For example, you may experience faster frame rates, smoother animations, and fewer crashes or glitches.
– Fixing bugs and security issues that may affect your graphics card or system. For example, you may resolve compatibility problems, prevent overheating or freezing issues, and protect your system from malicious attacks.
– Enabling new features and enhancements for your graphics card and applications that use it. For example, you may access higher resolutions, better graphics quality, and support for new technologies such as ray tracing or virtual reality.
Updating a graphics driver in Windows can help you get the most out of your graphics card and improve your overall user experience. In this guide, we will show you how to restart, reset or update the graphics driver in Windows 11/Windows 10.
How to Restart the Graphics Driver Using a Hotkey
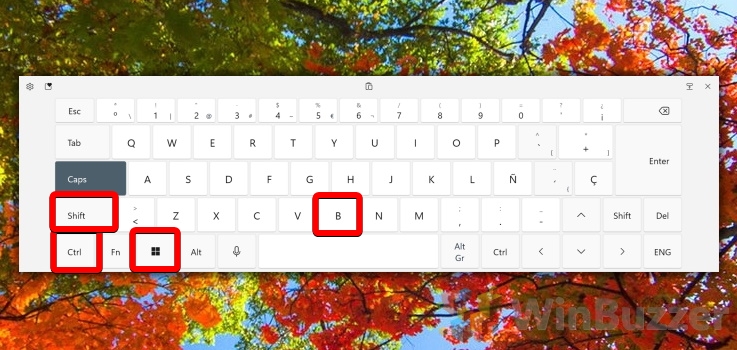
You can restart the graphics driver on Windows 10 and 11 by using the “reset graphics driver shortcut” of Windows. This method is simple and fast, but it requires some attention to avoid unwanted consequences. The keyboard shortcut to restart the graphics driver is “Windows + Ctrl + Shift + B”.
When you press this key combination, your screen will go black for a split second and you might hear a beep. This means that your graphics driver has been refreshed and reloaded. However, this also means that any settings or customizations you have made to your graphics driver may be lost. Therefore, you should save your work and close any applications that use the graphics driver before using this shortcut. Additionally, you should only use this shortcut when encountering a problem with your graphics driver, such as a crash or a glitch. Restarting the graphics driver too frequently may cause instability or performance issues.
How to Reset the Graphics Driver With Device Manager
When you reset the windows graphics driver with Device Manager, you are essentially uninstalling and reinstalling the driver software for your graphics card. This can help resolve poor performance, glitches, crashes, or compatibility problems with certain applications or games.
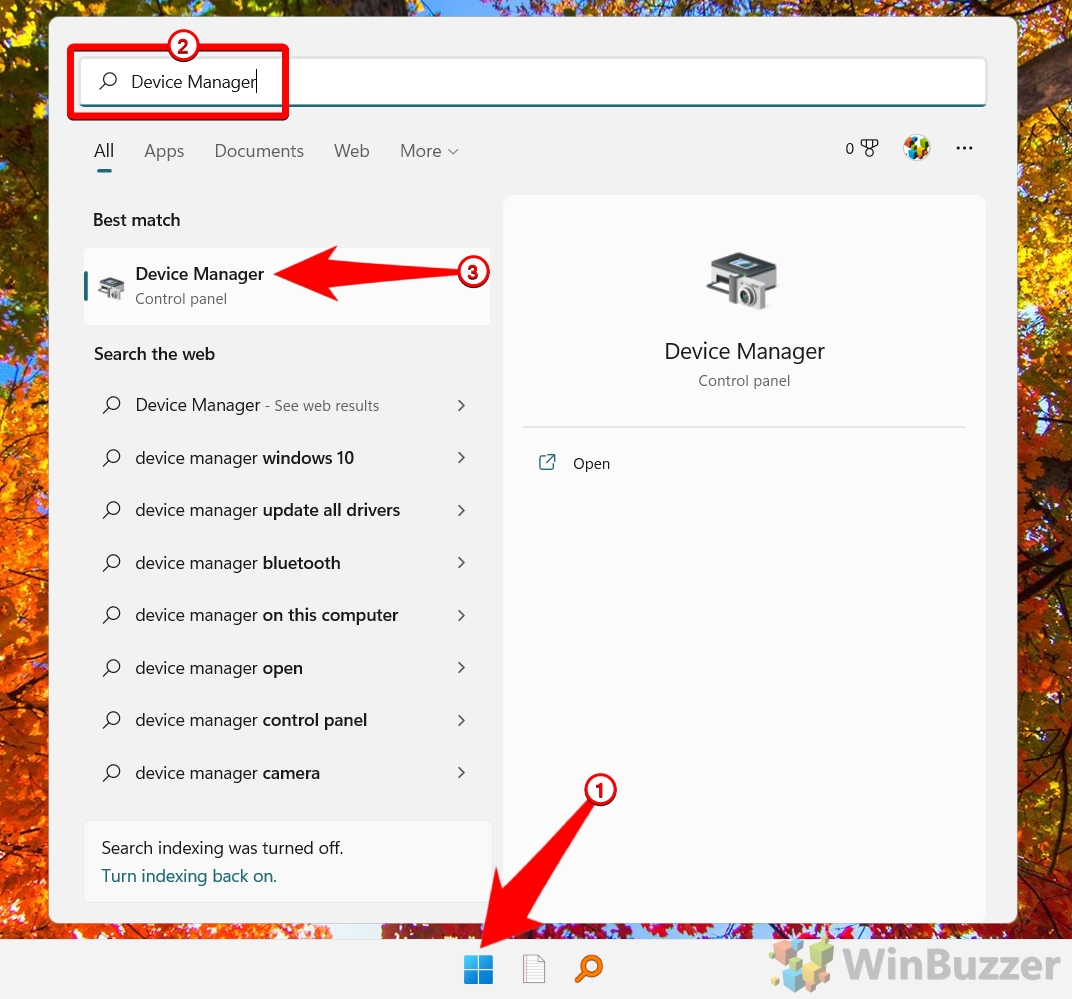
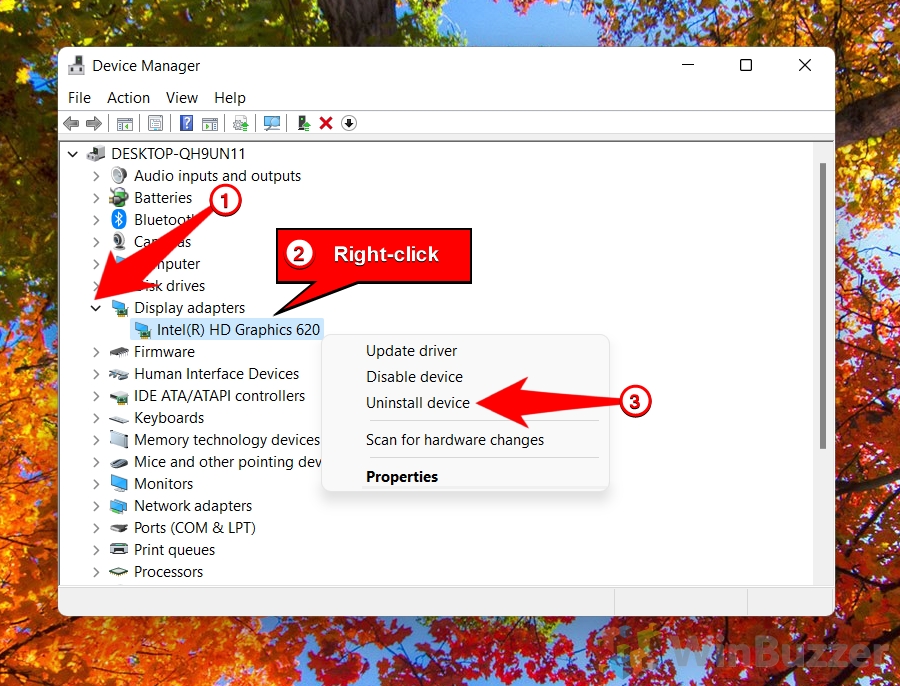
- Open “Device Manager” using Windows search

- Expand the list “Display adapters”, right-click your graphics card/chipset, and select “Uninstall device”
Then, restart your computer, and Windows will automatically reinstall the driver for you in its latest version. Alternatively, you can also download and install the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website after uninstalling the old one.

How to Reset the Graphics Driver via Windows Settings
If you are using a specific graphics driver software package that includes an application to set and fine-tune the functioning of your graphics chipset, you can reset the Windows graphics driver by uninstalling this Software via settings.
- Open Windows 11/Windows 10 settings and there “Add or remove programs”

- Uninstall graphics software to reset graphics driver
Find the graphics driver software, click on the three dots on the right side and click “Uninstall”. You will have to reboot your system to finish the procedure.

How to Update the Graphics Driver in Windows 11 or Windows 10
Updating the graphics driver in Windows 11 or Windows 10 is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, compatibility with the latest games and applications, and access to new features and bug fixes provided by the hardware manufacturer. This process involves obtaining and installing the latest driver version, either through Windows Update, Device Manager, or directly from the manufacturer’s website, to keep your graphics system running smoothly and efficiently.
Option 1: Using Windows Update to Update the Graphics Driver
Windows Update is a reliable method to update your graphics driver, as it provides updates approved by Microsoft, ensuring compatibility and stability. This method is the simplest and is recommended for most users because it minimizes the risk of installing incorrect or unstable drivers.
- Open Windows Update
Navigate to the “Settings” menu by clicking on the Start menu and selecting the gear icon. Once in Settings, go to “Update & Security” and then click on “Windows Update“. - Check for Updates
Click on the “Check for updates” button. Windows will automatically search for available updates, including graphics driver updates. If an update is available, it will be listed under the available updates. - Install the Graphics Driver Update
If a graphics driver update is available, it will either be installed automatically or you may need to click on the “Download and install” link. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Option 2: Using Device Manager to Update the Graphics Driver
This method gives you more control over the driver update process, allowing you to specifically select the graphics driver for an update. It’s particularly useful if Windows Update hasn’t provided a recent driver update or if you’re troubleshooting graphics-related issues.
- Open Device Manager
Right-click on the Start menu and select “Device Manager” from the context menu. This opens the Device Manager window, where you can view and manage hardware devices. - Locate the Graphics Driver
Expand the “Display adapters” section by clicking on the arrow next to it. This will reveal your graphics card(s). Right-click on your graphics card and select “Update driver“. The steps are similar to resetting your graphics driver, as shown above. - Search Automatically for Drivers
Choose the option to “Search automatically for updated driver software“. Windows will search your computer and the Internet for the latest driver software for your device. Follow the prompts to install any found updates.
Option 3: Updating Graphics Driver via Manufacturer’s Website
Downloading drivers directly from the manufacturer’s website ensures you get the latest drivers, often even newer than those available through Windows Update. This method is recommended for advanced users or when the above methods don’t provide the latest driver version.
- Identify Your Graphics Card
Before you can download the correct driver, you need to know the make and model of your graphics card. Follow our other guide on how to check which graphics card you have to identify your exact model or chipset. - Visit the Manufacturer’s Website
Go to the website of your graphics card’s manufacturer (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, etc.). Navigate to the “Drivers” or “Support” section of the site. - Download and Install the Driver
Select your graphics card model and your Windows version to find the correct driver. Download the driver, typically available as an executable (.exe) file. Once the download is complete, open the executable file and follow the on-screen instructions to install the driver.
Common Display Driver Software Packages for Windows 11 and Windows 10
- Intel Graphics Driver: This is the official driver package for Intel integrated graphics processors (IGPs), which are commonly found in laptops and low-end desktops. Intel Graphics Driver drivers enable basic graphics functionality and support for Windows features such as HDR and WDDM 2.7. They also include features such as Intel Graphics Command Center, which allows users to adjust their display settings and preferences.
- Intel HD Graphics Driver: Apart from the Intel Graphics Driver, Intel also provides HD Graphics Drivers for older integrated graphics, which are common in previous generations of laptops and desktops. These drivers support basic display functionalities and some of Intel’s older integrated graphics features.
- Intel Iris Xe Graphics Driver: For systems equipped with Intel’s newer Iris Xe graphics solutions, which offer improved performance over traditional integrated graphics. These drivers support advanced features and are aimed at providing a better gaming and multimedia experience on thin-and-light laptops.
- NVIDIA GeForce: This is the official driver package for NVIDIA graphics cards, which are widely used for gaming and professional applications. NVIDIA GeForce drivers offer optimal performance, compatibility, and stability for NVIDIA GPUs. They also include features such as GeForce Experience, which allows users to optimize their games settings, record and stream gameplay, update drivers and more.
-
NVIDIA RTX/Quadro Driver: Specifically designed for NVIDIA’s Quadro series of graphics cards, now called NVIDIA RTX, which are targeted towards professionals in CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CG (Computer Graphics), DCC (Digital Content Creation), and visualization applications. These drivers are optimized for stability and performance in professional applications.
-
NVIDIA Studio Driver: Aimed at creative professionals, NVIDIA Studio Drivers are designed to provide the best performance and reliability when working with creative applications like Adobe Photoshop, Premiere Pro, and others. They are tested extensively with creative software applications to ensure maximum performance and stability.
-
NVIDIA RTX Enterprise Driver: Similar to Quadro drivers but tailored for the newer RTX series, these drivers are intended for professionals and enterprises requiring maximum performance and reliability in demanding computing tasks, including AI, deep learning, and high-performance computing (HPC).
- AMD Radeon Software: This is the official driver package for AMD graphics cards, which are also popular among gamers and professionals. AMD Radeon Software drivers provide high-quality graphics performance, support for DirectX 12 and Vulkan APIs, and enhanced features such as Radeon Boost, which dynamically adjusts resolution to improve frame rates in fast-paced games.
- AMD Adrenalin Edition: This is an updated or alternative branding for AMD’s graphics drivers and software suite, previously known as AMD Radeon Software. It includes a comprehensive set of tools for optimizing performance and visual quality, along with features like Radeon Anti-Lag, Radeon Image Sharpening, and AMD Link for connecting to devices and streaming games.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Graphics Drivers
What should I do if my screen remains black after resetting the graphics driver?
If your screen doesn’t recover after using the reset shortcut, wait a few moments as it might take some time. If the issue persists, try a forced restart of your computer by holding down the power button.
Can updating the graphics driver improve gaming performance?
Yes, updating your graphics driver can lead to better gaming performance by providing optimizations for new games, fixing bugs, and sometimes unlocking new features that enhance graphics quality and frame rates.
How do I know if my graphics driver needs an update?
Check for updates regularly on the manufacturer’s website, or use dedicated software like Intel Graphics Driver Software, NVIDIA GeForce Experience or AMD Radeon Software. Also, stay informed about updates when experiencing graphics-related issues or when new games or software don’t perform as expected.
Is there a way to automate graphics driver updates?
Yes, both NVIDIA and AMD offer utilities (GeForce Experience for NVIDIA and Radeon Software for AMD) that can automatically check for and apply driver updates. Windows Update can also provide driver updates, though these may not be the most current.
What’s the difference between a clean installation and a regular update of a graphics driver?
A clean installation removes the previous driver version and its settings before installing the new one, potentially resolving conflicts or issues. A regular update overlays the new driver on top of the old one, retaining settings.
How can I revert to a previous graphics driver version if an update causes issues?
You can roll back the driver in Device Manager by right-clicking the graphics device, selecting “Properties“, going to the “Driver” tab, and clicking “Roll Back Driver“, if available.
What are the risks of using outdated graphics drivers?
Using outdated drivers can lead to security vulnerabilities, decreased performance, and compatibility issues with new software or games, potentially resulting in crashes or suboptimal performance.
Can I use third-party software to manage my graphics drivers?
While third-party utilities exist for driver management, it’s generally recommended to use official software from the hardware manufacturer or Windows Update to avoid potential issues with compatibility or security.
How do integrated and dedicated GPUs affect driver updates?
Systems with both an integrated and a dedicated GPU might require updates for both drivers. Ensure you update the correct driver corresponding to the GPU in use for specific applications or games.
What precautions should I take before updating my graphics driver?
Create a system restore point before updating so you can revert to the previous state if the update causes system instability or other issues.
Can driver updates fix hardware-related issues?
While updates can resolve software conflicts and improve compatibility, they cannot fix physical damage or wear to the graphics hardware itself.
How do I disable automatic driver updates in Windows?
To prevent Windows from automatically updating your drivers, you can change the system settings via the Control Panel under “System > Advanced system settings > Hardware tab > Device Installation Settings“, and choose “No“.
What to do if a graphics driver update fails to install?
If an update fails, try downloading the driver directly from the manufacturer’s website and perform a clean installation, or check for any specific error messages for targeted troubleshooting.
How can I check the version of my installed graphics driver?
Open Device Manager, expand “Display adapters“, right-click your graphics device, select “Properties“, and go to the “Driver” tab to see the driver version.
Why might a graphics driver update not show improvements immediately?
Some updates target specific issues or applications. If the update doesn’t address your particular use case, you might not notice immediate improvements. Additionally, system restarts or specific application settings adjustments might be necessary to see changes.
Related: How to Update and Download Nvidia Drivers without GeForce Experience
In our other guide we show you how to download Nvidia Drivers without Geforce experience, as well as how to install them and check your GPU. If you want to know how to update Nvidia drivers without Geforce Experience, the manual installation of a new driver will exactly do that and replace your existing outdated Nvidia GPU driver.
Last Updated on April 21, 2024 11:13 am CEST by Markus Kasanmascheff