Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling is a Windows 11 and 10 feature that first appeared in 2020. You may be wondering what it does, whether you should turn GPU scheduling or off, and how to disable or enable hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling on your PC. We’ll be covering all this today, starting with a short explanation of how it works.
What Is Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling?
Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling is a feature designed to allow better GPU scheduling between applications, theoretically improving gaming and video performance.
To understand how it works, you first need to know how Windows previously did things. The OS has long offloaded some graphically intensive tasks to the GPU so that games, videos, and photo/video editing apps run smoothly.
The CPU looks at all the frames that need to be rendered by the GPU, orders, and prioritizes them, and sends them off one by one for processing. Tasks like this are why the CPU is often referred to as the “brains” of your computer.
In recent years, however, consumer GPUs have become more and more capable of performing their own tasks.
When you enable hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling in Windows 11, your PC instead uses a GPUs own dedicated scheduling processor and memory (VRAM) to gather and order the data. This both frees the CPU to perform other tasks and reduces latency.
Should I Turn Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling On or Off?
The simple answer is “it depends”. Currently, testing shows that hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling has little impact on performance on high to medium-end machines. On lower-end machines, however, you may see a reduction in latency and therefore stuttering in games and videos.
Unfortunately, while you’ll see improvements (however minor) in most titles, there are some reports that it can negatively impact the experience in others. Ultimately, it’s something you will just have to test with the tasks and hardware you have. If it doesn’t work out, you can always toggle it again.
Before you do, you should know that hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling in Windows 10 and 11 requires a modern GPU. For Nvidia, that means a GTX 1000 or later card, and for AMD 5600 series or later. If you’re set on the requirements front, we’ll show you how to turn on or off hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling using two methods below:
How to Enable Hardware-accelerated GPU Scheduling in Windows 11 via the Registry
Though it’s not the most intuitive way, turning hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling on or off using the registry is still relatively easy. As a bonus, the steps outlined below will be exactly the same on Windows 10 and Windows 11, so you can follow along easily on either OS. Let’s get started:
- Press Start and type “Regedit”, then click the top result
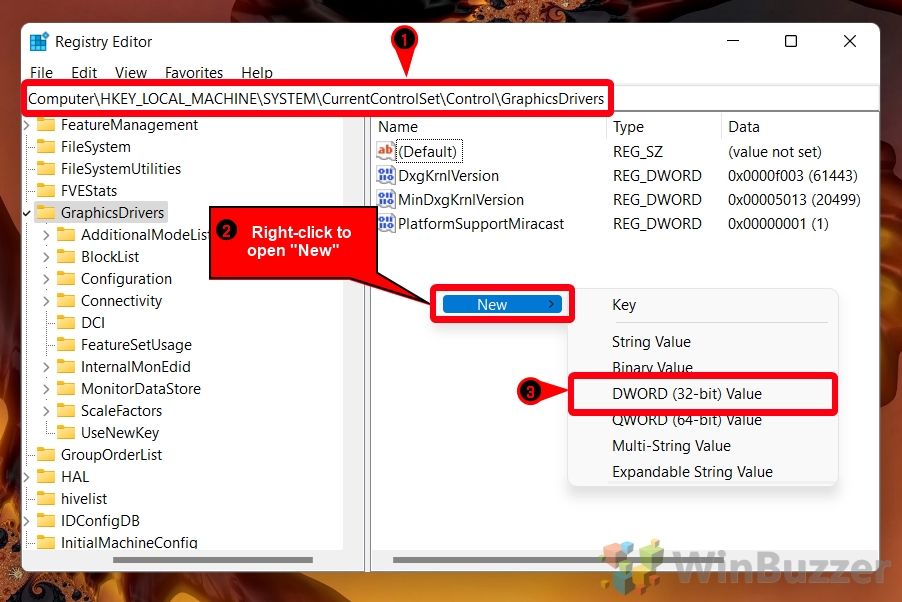
- Browse to the “GraphicsDrivers” registry key and create a new DWORD
You’ll find the GraphicsDrivers key inComputer/HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SYSTEM/CurrentControlSet/Control/GraphicsDrivers. To add the DWORD, right-click any blank space in the main pane and choose “DWORD (32-bit) Value”.
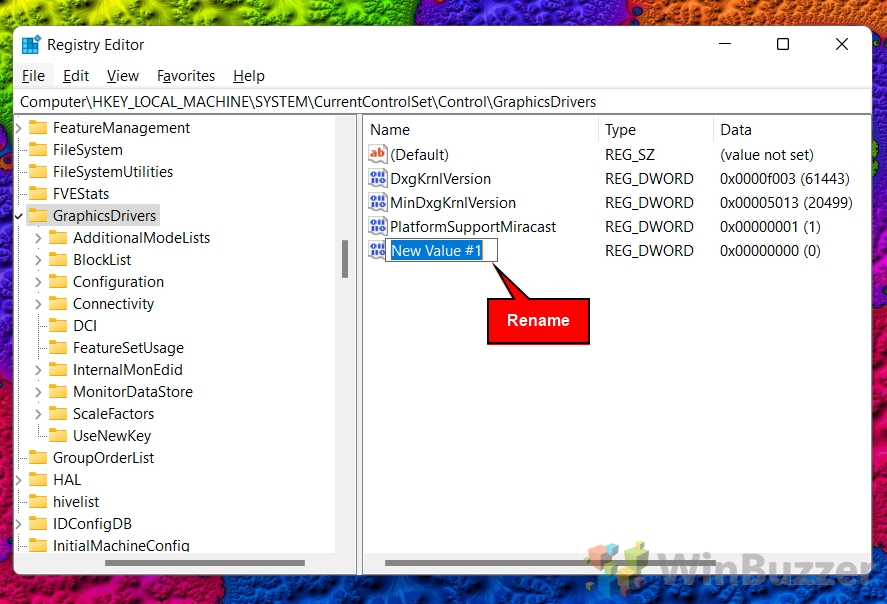
- Name the new DWORD “HwSchMode”
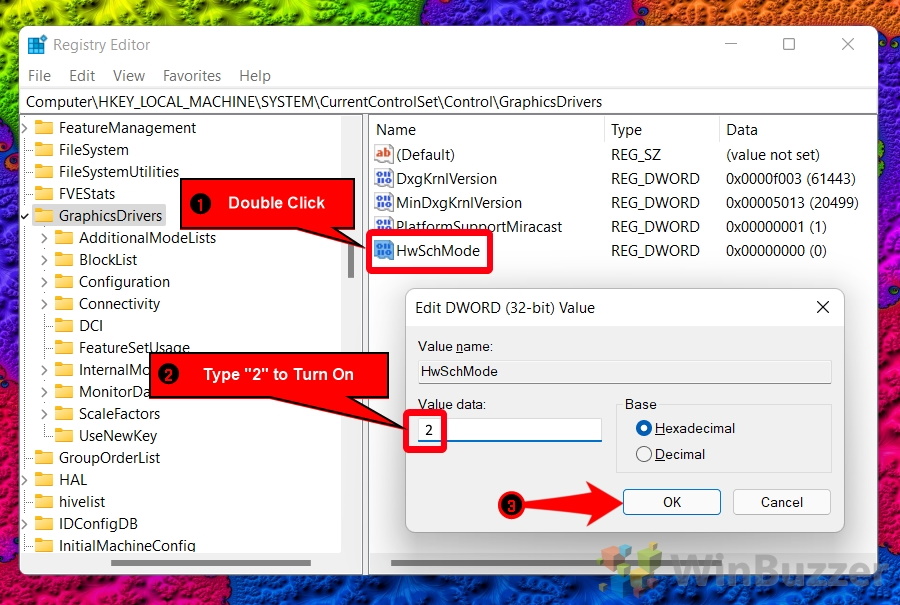
- Turn on hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling by changing the value data to “2”
Double-click on its name to modify your DWORD’s value data, then press “OK” once you’ve entered “2” in the value data field.
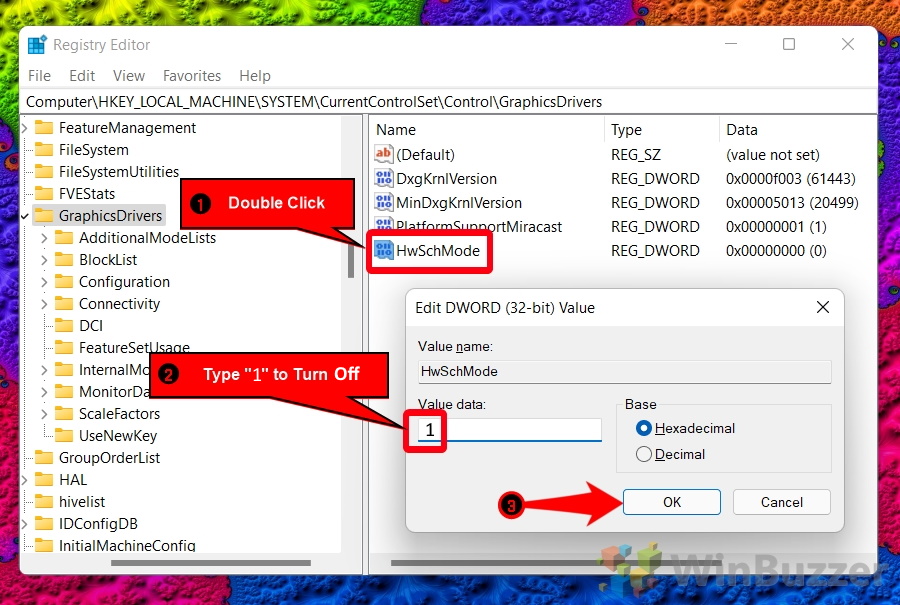
- Turn off hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling by changing the value data to “1”
To turn the GPU scheduling off, double-click your DWORD and enter “1” in the value data field, then press “OK”.
How to Disable or Enable Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling in Windows 11 Settings
The easiest way to turn hardware GPU scheduling on or off is through Windows 11’s beautiful new Settings interface. Of course, you can also do this in Windows 10, but your layout and labels may differ.
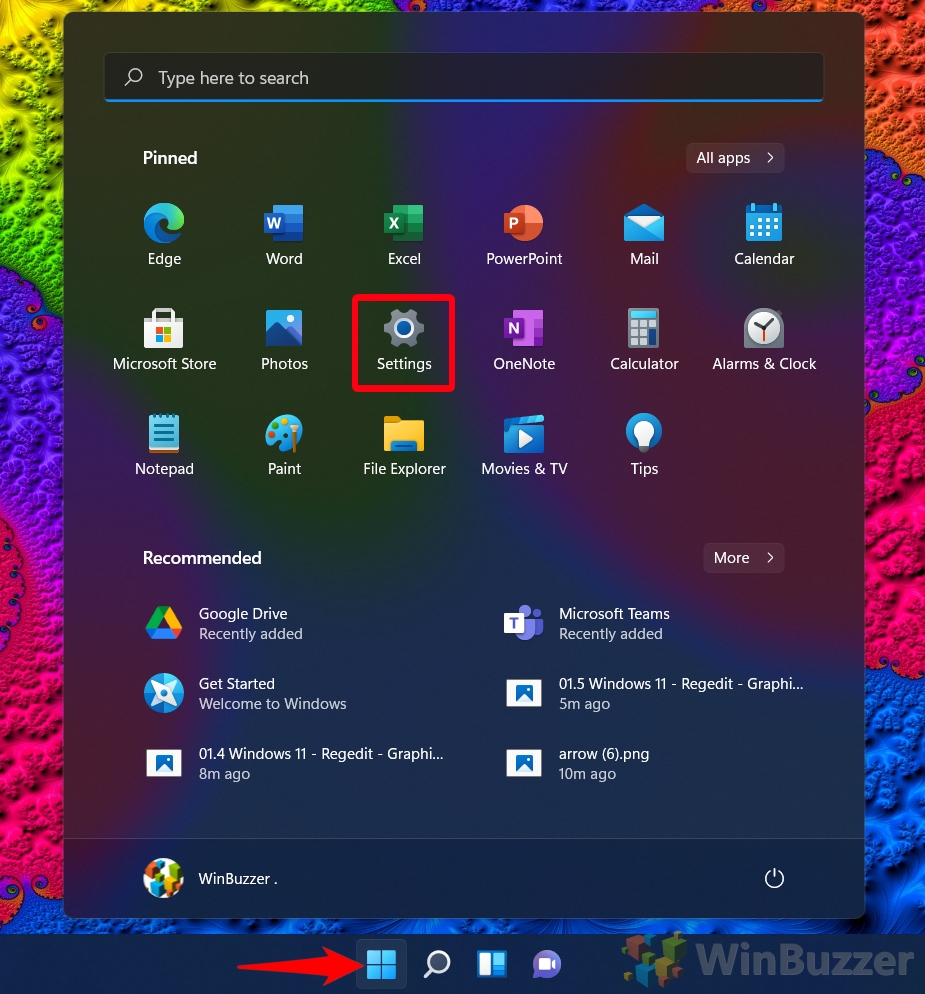
- Open Settings
Press Start and press the “Settings” icon on your Start menu. Alternatively, press “Windows + I”.
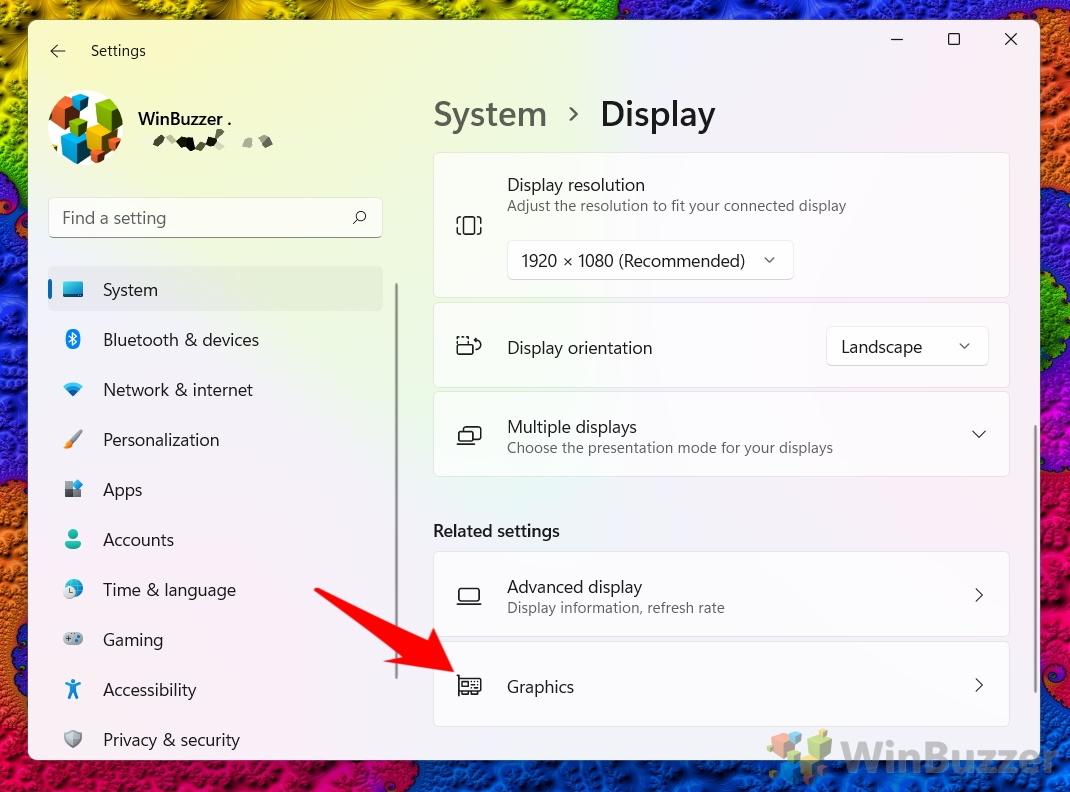
- Click “System” in the settings sidebar, then on “Display” in the main pane
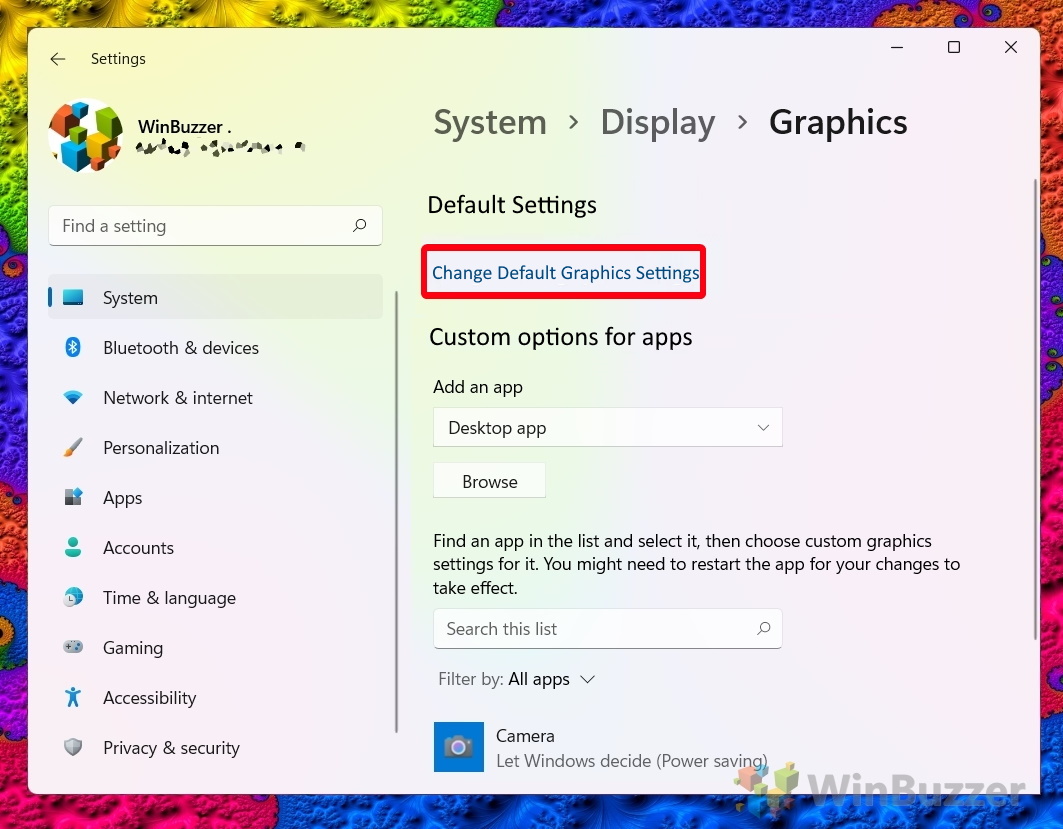
- Click on the “Graphics” heading
- Press “Change Default Graphics Settings”
- Turn hardware GPU schedule on or off via the toggle
Moving the toggle to the right will turn the feature on, and to the left off.

FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling
Do I need to update my GPU drivers to use Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling?
Absolutely. For Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling to function correctly and for your system to recognize and utilize the feature efficiently, it’s critical to have the most current GPU drivers installed. Manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD routinely update their drivers to optimize performance and compatibility with Windows features, including this specific scheduling option.
What are the potential downsides of enabling Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling on older hardware?
While Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling is designed to optimize GPU task management and potentially improve performance, its effectiveness is predominantly noticeable in newer hardware. On older systems, this feature may not significantly boost performance and, in some instances, could lead to stability or compatibility issues. It’s essential to monitor your system’s response closely after enabling the feature, especially if you’re running on hardware that’s near or below the recommended specifications.
Can enabling this feature lead to higher GPU temperatures?
Given that Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling allows the GPU to manage its queue, leading to potentially more efficient processing of tasks, there could be a marginal increase in GPU workload, which might translate to slight increases in temperature. However, this change is usually within safe operational parameters. If excessive temperatures are observed, it’s advisable to check for adequate cooling or reduce the workload.
How can I test the effectiveness of Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling on my system?
To assess the impact of Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling, conduct benchmark tests before and after enabling the feature using applications or games that heavily rely on GPU performance. Monitor for changes in frame rates, application responsiveness, and video playback quality using benchmarking tools. Additionally, observe if there’s a noticeable decrease in CPU usage, which can indicate effective offloading of tasks to the GPU.
Can Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling improve the performance of video streaming services?
For video streaming, the performance boost from enabling Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling might be less apparent to the end-user but can contribute to smoother playback and reduced CPU load, especially in high-resolution streaming. The extent of the improvement largely depends on the streaming application’s optimization for leveraging GPU capabilities.
How do I check which GPU series I have installed on my system?
To identify your GPU series and model, access the Device Manager through the Windows search bar, expand the “Display adapters” section, and your GPU’s details will appear. For more comprehensive information, such as the driver version and supported features, you can also use proprietary software provided by the GPU manufacturer or third-party system information tools.
Does the performance improvement from enabling Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling vary across different GPU models?
Yes, the degree of performance enhancement can significantly differ between GPU models. Modern GPUs, especially those designed with dedicated scheduling hardware, tend to benefit more from this feature, as they can more efficiently manage task queues. Older models may see limited or no improvement, making it crucial to evaluate the feature’s impact on a case-by-case basis.
Is Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling beneficial for professional graphics work, like 3D modeling?
Professionals working on graphics-intensive applications such as 3D modeling and rendering may experience smoother operations and reduced application latency. This is especially true for workloads that can take full advantage of GPU resources. However, the tangible benefits can depend on the specific software’s ability to leverage the GPU efficiently and the complexity of the tasks being processed.
Is a system restart required after toggling Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling?
Yes, after enabling or disabling Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling, a system restart is necessary to apply the changes effectively. This ensures that the GPU and related system components can reinitialize under the new configuration, allowing you to experience the adjusted performance dynamics immediately.
Are there specific Windows versions where Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling is more effective?
The feature is engineered to work on both Windows 10 and Windows 11. However, as both the operating system and drivers for your hardware receive updates, the effectiveness of this feature might improve over time. It’s more about the synergy between the operating system, the drivers, and the hardware rather than the Windows version alone.
If I experience issues after enabling Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling, what should I do?
If you encounter problems such as system instability, graphical glitches, or performance drops, the first step is to ensure your GPU drivers are fully updated. If issues persist, reverting to the default settings by disabling the feature may help. For persistent or complex problems, consulting with the GPU manufacturer’s support or exploring online communities for similar experiences can offer additional troubleshooting insights.
Can Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling be used on integrated GPUs?
While primarily beneficial for discrete GPUs, integrated GPUs in newer processors may also support and benefit from Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling. However, the performance improvements might be less noticeable due to the integrated GPU’s inherent limitations compared to more powerful discrete options.
Does Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling require any specific BIOS settings?
Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling is a Windows feature that doesn’t necessitate changes to BIOS settings. It operates within the Windows environment, assuming your hardware meets the necessary specifications and your drivers are up to date.
How do games and graphics applications detect if Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling is enabled?
Games and applications indirectly benefit from the feature through the system’s more efficient task scheduling and potentially reduced latency. They do not detect the feature’s status but can take advantage of the possibly improved performance environment it facilitates.
Can Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling impact the performance of other applications running in the background?
By allowing the GPU to manage its task scheduling more autonomously, Hardware-Accelerated GPU Scheduling can reduce the CPU’s workload, potentially freeing up resources. This can have a positive impact on background application performance, especially in multitasking scenarios, by allocating resources more efficiently across operations.
Related: How to Enable or Disable Hardware Acceleration in Chrome
Hardware acceleration makes use of your computer’s graphics card to speed up the browser and free up your CPU. As your GPU is designed to perform video-based calculations, it’s often better suited for tasks like watching videos or playing browser games. In our other guide, we explain what hardware acceleration is, when you should turn it off, and how you can enable or disable it in Google Chrome.How to Enable or Disable Hardware Acceleration in Chrome.
Related: How to Restart, Reset or Update the Graphics Driver in Windows 11 or Windows 10
Restarting a graphics driver in Windows involves sending a special signal to the graphics hardware, which causes it to stop processing any commands and release any resources it is currently using. Then, Windows unloads the driver software from memory and reloads it again. You can also uninstall a graphics driver in Windows 11/Windows 10 to reset it to its original version. In our other guide, we show you how to restart the graphics driver in Windows without rebooting and how to reset or upgrade the graphics driver if it does not work properly.
Related: How to Update and Download Nvidia Drivers without GeForce Experience
though Nvidia strongly pushes GeForce Experience on its GPU owners, it’s possible to update them without it. The process is a bit more involved, but GTX drivers can be found on its official website for installation. Doing so will still net you the use Nvidia Control Panel, but won’t come with extra fluff like desktop overlays, settings optimizers, and game recording. In our other guide, we show you how to download Nvidia drivers without GeForce Experience and help you check your hardware.
Last Updated on March 31, 2024 3:22 pm CEST by Markus Kasanmascheff