Whether you’re looking to protect sensitive information or keep data private from other users, it’s important to encrypt the folders and files on your PC. In Windows 11 and Windows 10, the strongest native protection is the Encrypting File System (EFS).
What is EFS Windows Encrypting File System?
The Encrypting File System (EFS) is a Windows file encryption feature of the NTFS filesystem that you can utilize to encrypt a folder or file. It allows a user to make use of advanced yet standardized encryption algorithms to ensure others can’t access their data without a decryption key.
By default, no files in Windows are EFS encrypted. Instead, users must learn how to encrypt a folder manually. When you encrypt a folder, all new files saved to it will be encrypted automatically. Crucially, if the administrator changes the password of a user’s local account, that user will lose access unless the admin restores the encryption key.
It’s also worth noting that EFS encryption is only available on Windows 10 Pro, Education, and Enterprise editions. Regardless of your version, though, you cannot perform .zip file encryption. As soon as you use EFS on the file, it will be uncompressed. If you try to encrypt a zip a file that’s already encrypted, it will lose its encryption.
As an alternative, you can also use the Windows built-in Bitlocker-Tool to encrypt any drive completely so it won´t be accessible via any other OS like Linux or hacking-tools which are used to side-boot your PC.
⚠️ Please note: The process described below is the same in Windows 11 as it is in Windows 10. However, bear in mind that we’ll be using screenshots from Windows 10, so your UI may look a little different. We’ll point out any changes you need to be aware of as they come up.
How to Encrypt a Folder via Advanced Attributes
This method involves using the File Explorer’s interface to encrypt folders, making it user-friendly for those unfamiliar with command-line tools.
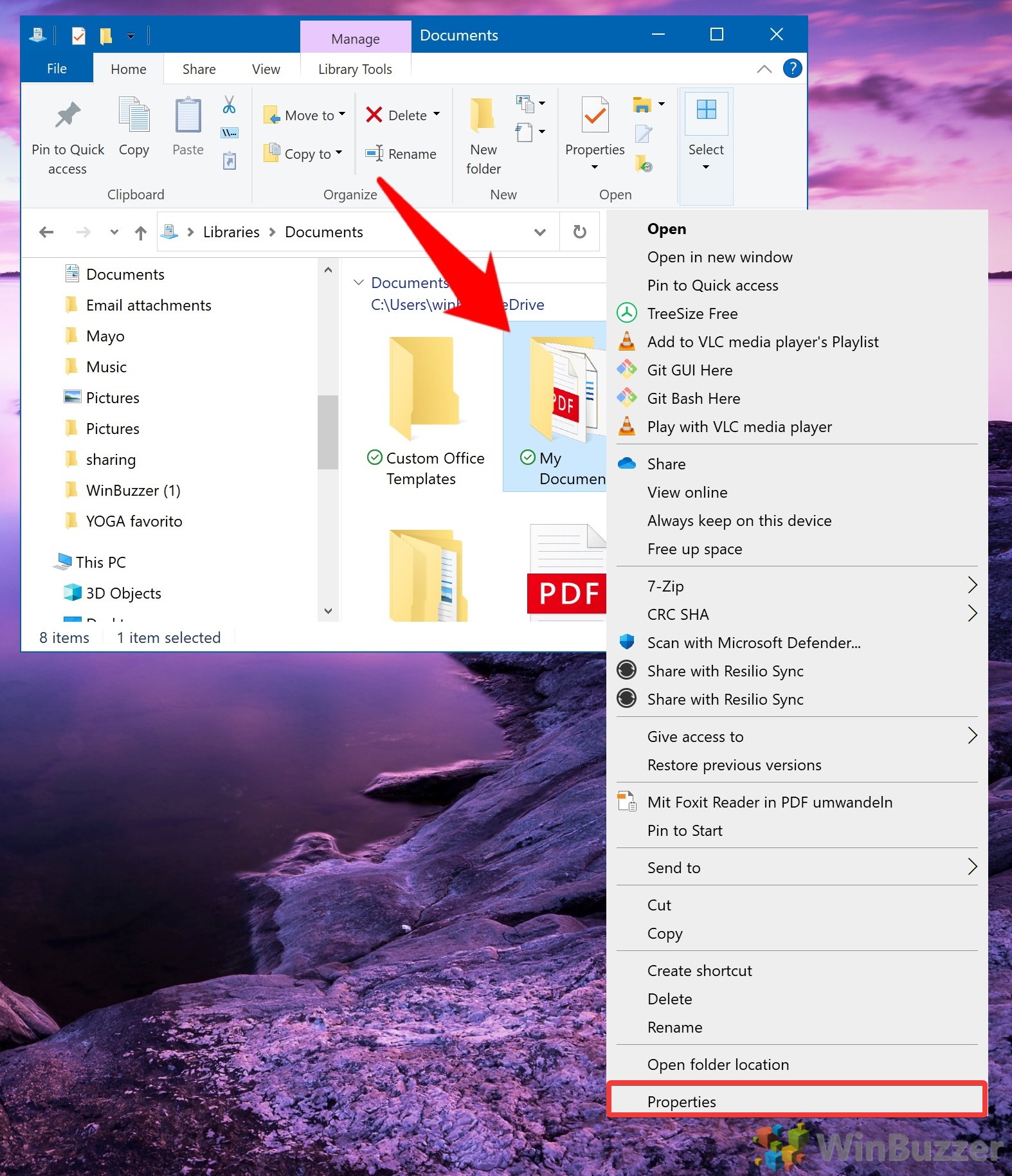
- Open the Folder’s Properties
Right-click the folder you wish to encrypt and select “Properties“. This action opens the folder’s properties window, where you can modify its attributes. In Windows 11, you first have to click “Show more options” to see the actual context menu.

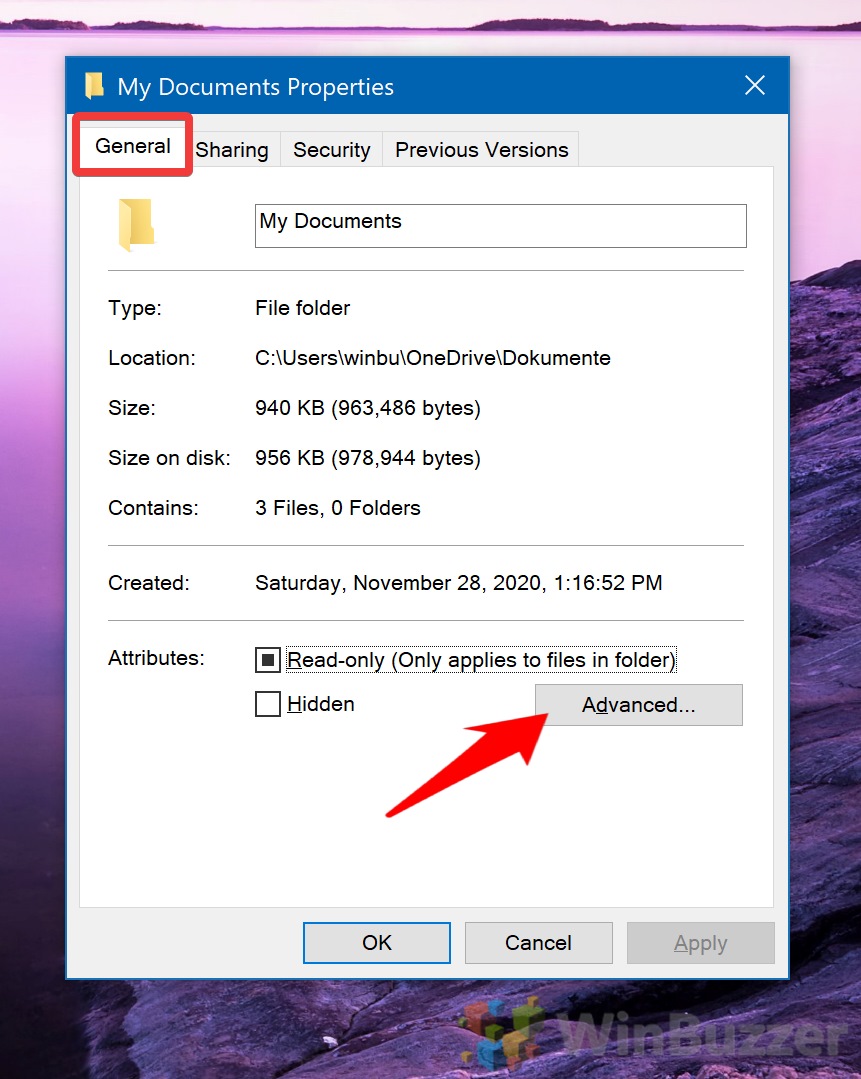
- Access Advanced Attributes
Navigate to the “General” tab and click on the “Advanced…” button. This opens the Advanced Attributes window, where you can adjust the encryption settings for the folder.

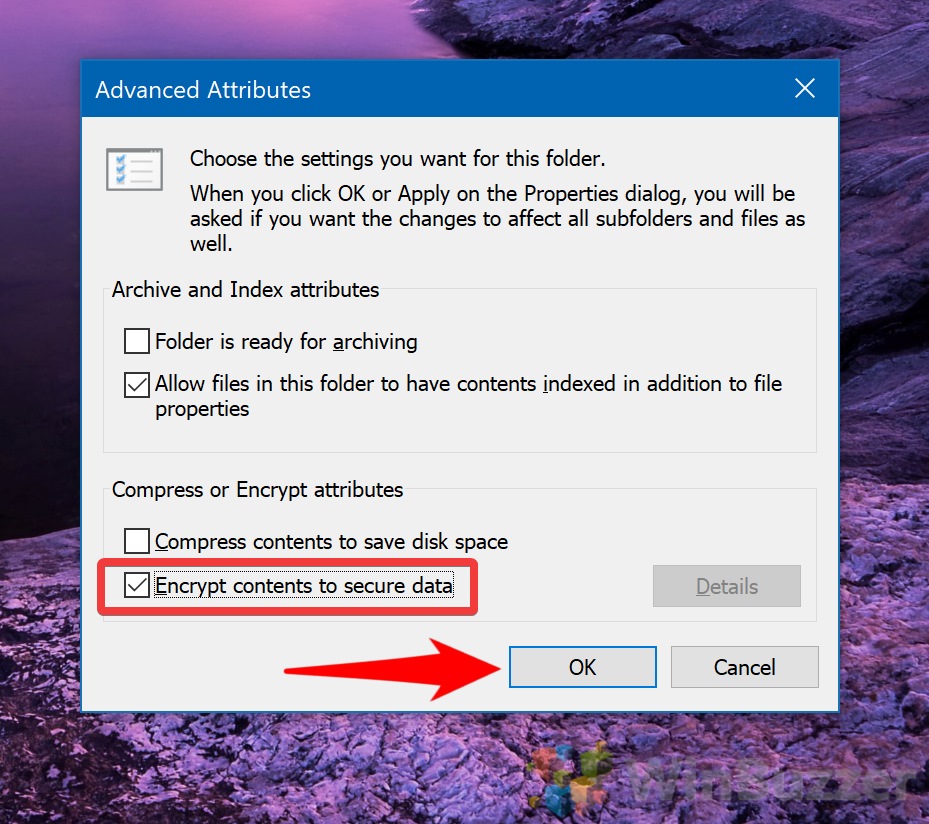
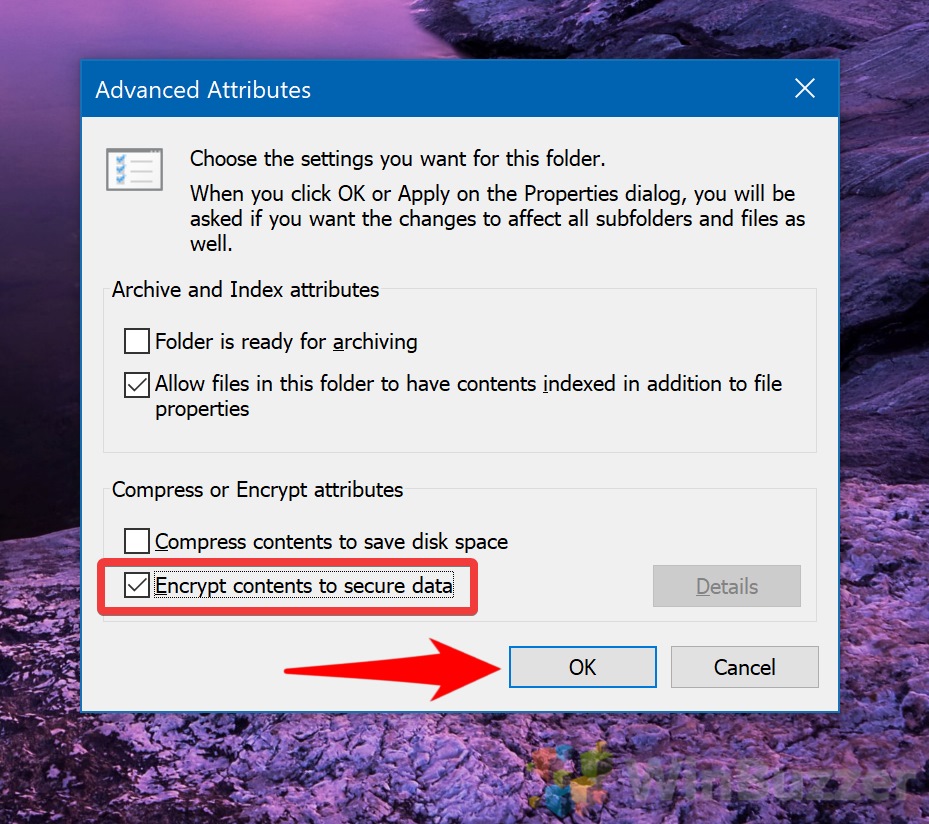
- Enable Encryption
In the Advanced Attributes window, check the “Encrypt contents to secure data” option under the “Compress or Encrypt attributes” section. Click “OK” to apply the encryption.

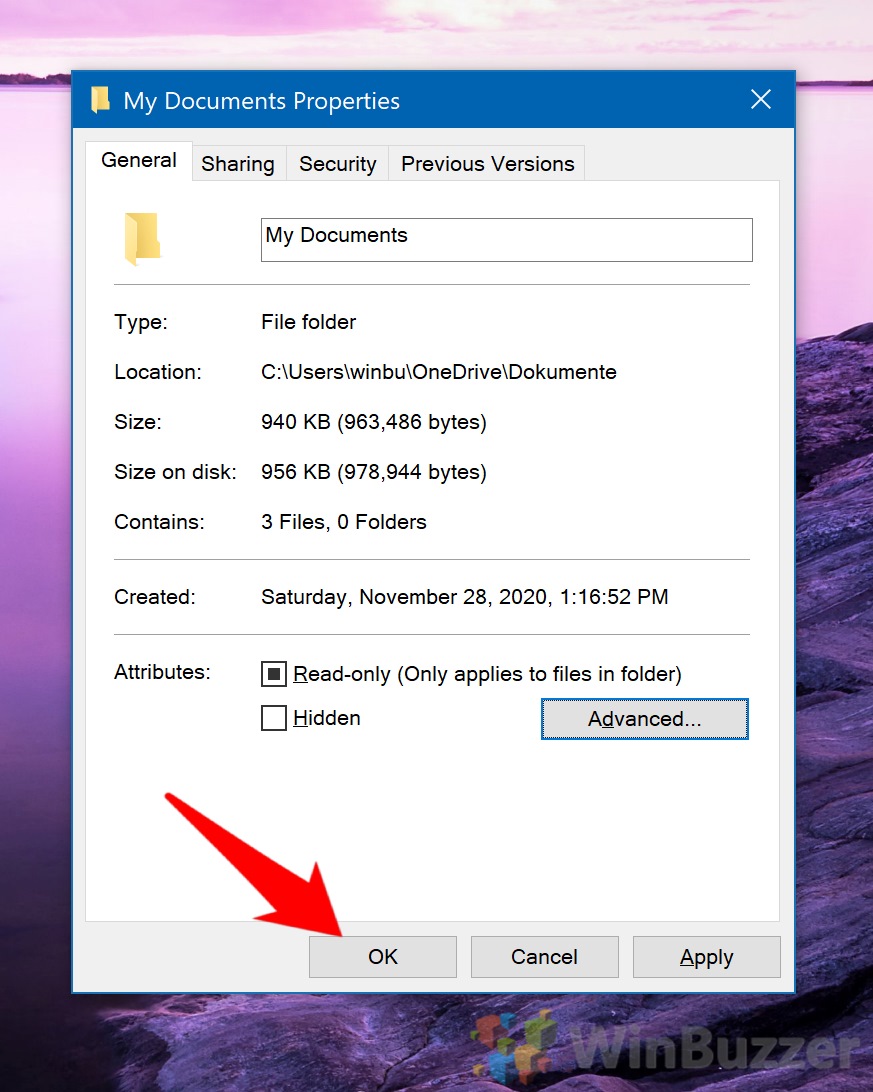
- Confirm Encryption
After enabling encryption, you’ll return to the folder’s properties window. Click “OK” again to finalize the encryption process.

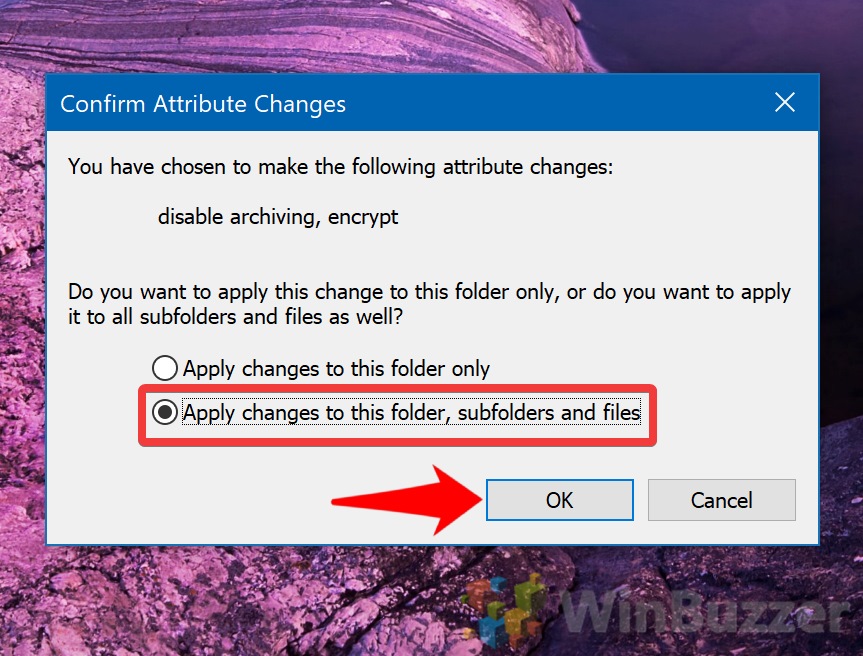
- Apply Encryption to Subfolders (Optional)
A dialog box may appear, asking if you want to apply the encryption to the folder only or include subfolders and files. Select “Apply changes to this folder, subfolders, and files” for comprehensive encryption.
The first option will only encrypt items in the top-level. For example, if you’re encrypting your documents folder, it will only apply it to the loose files. If you have a separate folder called “Work stuff”, it won’t be encrypted. The second option applies the changes to the top-level files, all subfolders, and files within them.

How to Encrypt Files via Advanced Attributes
Encrypting individual files follows a similar process to encrypting folders, providing an extra layer of security for specific documents or data.
- Open File Properties
Locate the file you want to encrypt, right-click on it, and choose “Properties” from the context menu.

- Open Advanced Attributes Settings
Within the file’s properties, go to the “General” tab and click on the “Advanced…” button to access encryption options.

- Encrypt the File
Check the “Encrypt contents to secure data” box in the Advanced Attributes window and click “OK” to enable file encryption. You may find that the encrypt contents to secure data option is grayed out on your PC. You will have toenable Windows File Encryption via NTFS EFS (Encrypting File System) on the filesystem-level first.

- Confirm Encryption in Properties
Back in the file’s properties window, click “OK” to apply the encryption settings.

- Encrypt File and Parent Folder (Optional)
A prompt may appear, giving you the option to encrypt just the file or the file and its parent folder. Choosing to encrypt both the file and its parent folder is recommended for enhanced security.
The second option applies the changes to all files in the same folder, and all subfolders, if there are any.

How To Encrypt Folder in Command Prompt
For users comfortable with the command line, encrypting folders via Command Prompt offers a faster, more direct method.
- Launch Command Prompt
Press the Start button, type “Command Prompt“, and open the application from the search results.

- Execute Encryption Command
Type the commandcipher /e "full\path\to\folder"to encrypt the specified folder. Add/sto the command (cipher /e /s "full\path\to\folder") if you want to encrypt subfolders and files within the folder as well.

How To Encrypt Files via Command Prompt
Command Prompt can also be used to encrypt individual files, providing a quick and efficient way to secure specific pieces of data.
- Open Command Prompt
Similar to the previous method, start by opening Command Prompt through the Start menu.

- Run Encrypt File Command
Typecipher /e "full\path\to\file"in Command Prompt, replacing “full\path\to\file” with the actual path of the file you wish to encrypt. This command encrypts the specified file.
If successful, you’ll see the message “1 file(s) [or directorie(s)] within 1 directorie(s) were encrypted”.

FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Windows EFS Encryption
Is EFS encryption available on Windows 11/10 Home edition?
No, EFS encryption is not available on Windows 11/10 Home edition. It is exclusively available on Windows 11/10 Pro, Education, and Enterprise editions. For Home edition users looking to encrypt their data, third-party encryption software or upgrading their Windows edition may be necessary.
Can I encrypt files on a USB drive using EFS?
Yes, files on a USB drive can be encrypted with EFS, provided that the USB drive is formatted with the NTFS file system and is connected to a PC that supports EFS, typically running Windows 10 Pro, Education, or Enterprise editions. Remember to back up your encryption keys if you plan to access the encrypted files on a different computer.
What happens if I forget the password to my encrypted file or folder?
If you forget your Windows account password, which is used to access EFS-encrypted files, you will need a previously backed up encryption certificate and key to decrypt the files. Without these backups, accessing the encrypted data will be incredibly difficult. Thus, securely storing your encryption certificate and key is crucial.
How can I share an EFS-encrypted file with another user?
To share an EFS-encrypted file, you must export your file encryption certificate and key, and the recipient must import them on their system. The recipient will then have the necessary permissions to decrypt and access the file. Detailed steps for exporting and importing encryption certificates can be found in Windows documentation.
Can I still use EFS to encrypt data if I’m logging in with a Microsoft account?
Yes, you can use EFS with a Microsoft account. The encryption and decryption process remains the same, irrespective of the account type. While using a Microsoft account, your encryption certificate and key are tied to your account, and it’s advisable to back them up for data recovery purposes.
How does EFS encryption interact with cloud storage and syncing services?
When using cloud storage or syncing services, EFS-encrypted files remain encrypted on the cloud. To access these files from another device, you will need the appropriate encryption certificate and key on that device. It’s important to note the encryption protects your data at rest, and you should ensure the cloud service provides secure transmission for complete security.
Is it possible to encrypt the entire drive using EFS?
EFS is designed for encrypting individual files and folders, and not for full-drive encryption. For encrypting an entire drive, it is recommended to use BitLocker, a different encryption feature provided by Windows. BitLocker encrypts all data on the drive, offering a comprehensive security solution.
Does EFS encryption protect my data from malware?
EFS effectively secures your data against unauthorized access but does not provide a defense against malware. If malware gains access to your system, especially with administrative privileges, it could potentially access or damage your encrypted files. Regular system scans and the use of anti-malware software are recommended for comprehensive protection.
Can I encrypt files on the network shares using EFS?
Yes, you can encrypt files located on network shares using EFS, provided the network share is on an NTFS volume and the machine hosting the share supports EFS. However, managing access and keys across different users and machines requires careful planning to ensure that authorized users can access the encrypted files when needed.
How do I recover an EFS-encrypted file if the user account is corrupted?
In the event of a user account corruption, recovering an EFS-encrypted file requires that you have previously backed up the encryption certificate and key. These backups can be imported into a new or repaired account to restore access to the encrypted data. Without these backups, data recovery would be highly complex and might require professional services.
What are the file system requirements for using EFS?
EFS requires the NTFS file system to operate because of its security and reliability features that support file-level encryption. EFS does not support other file systems like FAT32 or exFAT, making NTFS the necessary choice for users looking to utilize EFS encryption.
Can I use EFS in a non-domain environment, like a home PC?
EFS can be used effectively in a non-domain environment, such as on a home PC. EFS operates at the file system level and does not necessitate a connection to a corporate domain. Encryption keys are managed on the individual system, allowing for personal use and management.
How do I manage EFS-encrypted files if there are multiple users on the computer?
To manage access to EFS-encrypted files when there are multiple users on a computer, you can utilize the file’s encryption properties to add users who can decrypt the files. Each added user will need their own encryption certificate imported into the system. Managing encryption certificates for each user enables controlled access to encrypted data.
Are there any performance impacts when using EFS on large files or directories?
Encrypting large files or directories with EFS may lead to a slight performance impact during the initial encryption process due to the computational overhead of encrypting each file. However, once files are encrypted, this impact becomes negligible during regular access. It’s a trade-off between enhanced security and minimal performance implications.
Does EFS work with files encrypted on another machine within the same network?
EFS allows access to encrypted files from another machine within the same network, provided that the machine has the necessary encryption certificate and key. Moving encrypted files across the network requires careful management of encryption keys to ensure the files can be decrypted when accessed from different machines.
Related: How to Enable or Disable File Encryption in Windows (NTFS EFS)
You may find that the “Encrypt contents to secure data” option is grayed out on your PC. In our other guide, we show you how to enable or disable Windows File Encryption via NTFS EFS (Encrypting File System) on the filesystem-level for all users.

Related: How to Password Protect a Folder in Windows 11 and Windows 10
Protecting your sensitive data in Windows 11 and Windows 10 is crucial, especially if you’re sharing your PC with others or simply want to keep certain information confidential. While Windows 11 and Windows 10 don’t come with a dedicated feature for password-protecting individual folders, there are effective ways to secure your data. In our other guide, We show you how to password-protect a folder in Windows using different methods with built-in and third-party tools.
Related: How to Use OneDrive Personal Vault to Passwort-Protect Your Files
OneDrive Personal Vault adds an additional layer of security to your most important files. When users save a document or photo to their OneDrive vault, they can only access it via an additional method of authentication. In our other guide, we show you how to set up a OneDrive Personal Vault on Windows 11 or Windows 10.