While mobile phones typically have GPS built-in, that’s not usually the case for desktop and to an extent, laptop PCs. As a result, browsers often set your location incorrectly. In such cases, it’s useful to know how to change location in Google Chrome manually.
First, though, it’s worth understanding why this happens. You may notice that the map you’re accessing has your general area right, but not your specific street or even town. In lieu of a GPS, the next closest data point is your IP address. Depending on where your ISP’s closest exchange is, this could result in it being miles off course.
Thankfully, you can set your Google Chrome geolocation quite easily through its developer settings. By adjusting the HTML 5 geolocation setting, you can provide a better source of information for websites to use. Here’s how to change those location settings in Google Chrome:
How to Change Google Location Settings
Before we start, you should open a webpage that uses the HTML 5 geolocation API. The one we’ll be utilizing is by Best VPN. After allowing it access, you can follow the steps below to change location:
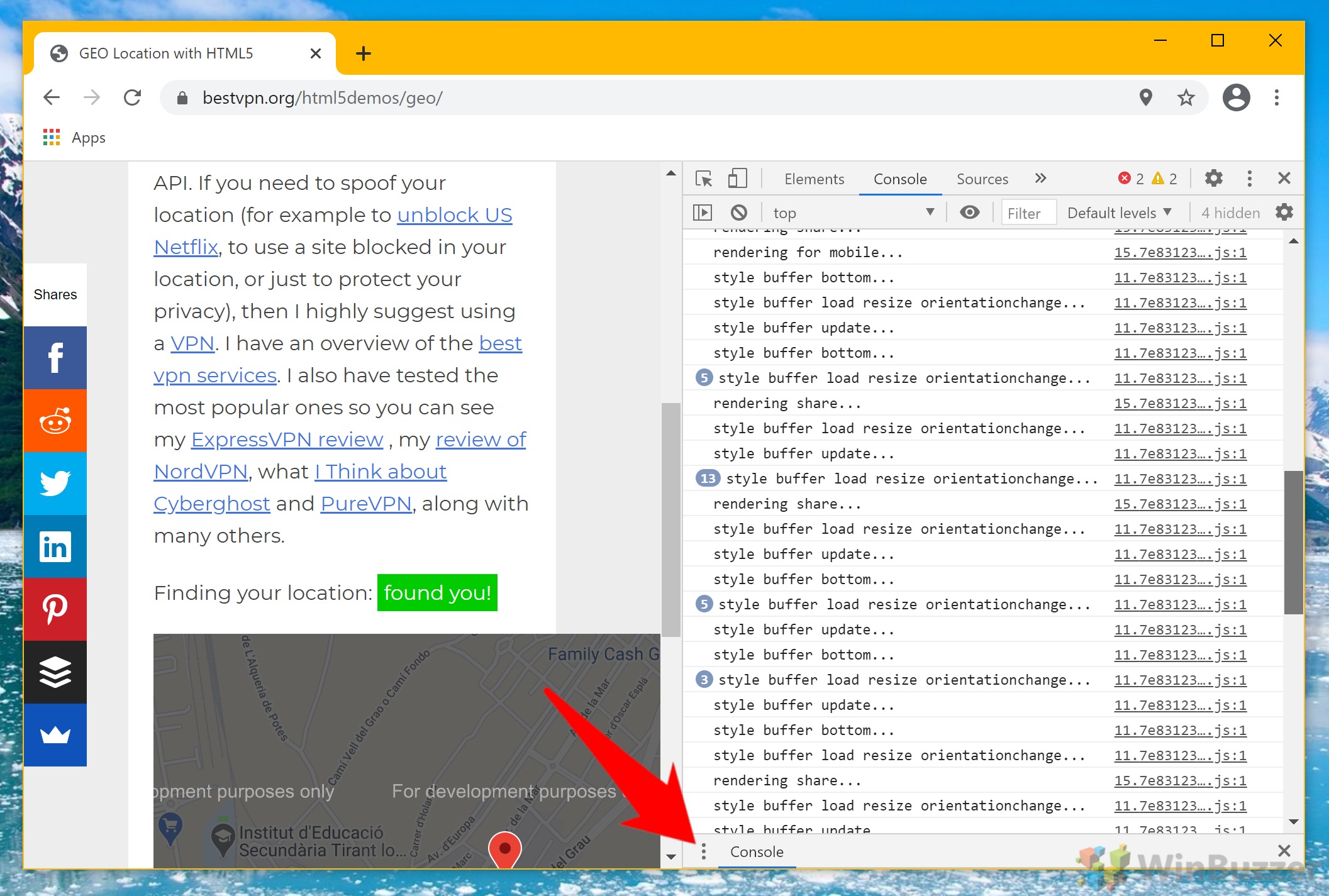
- Open developer settings
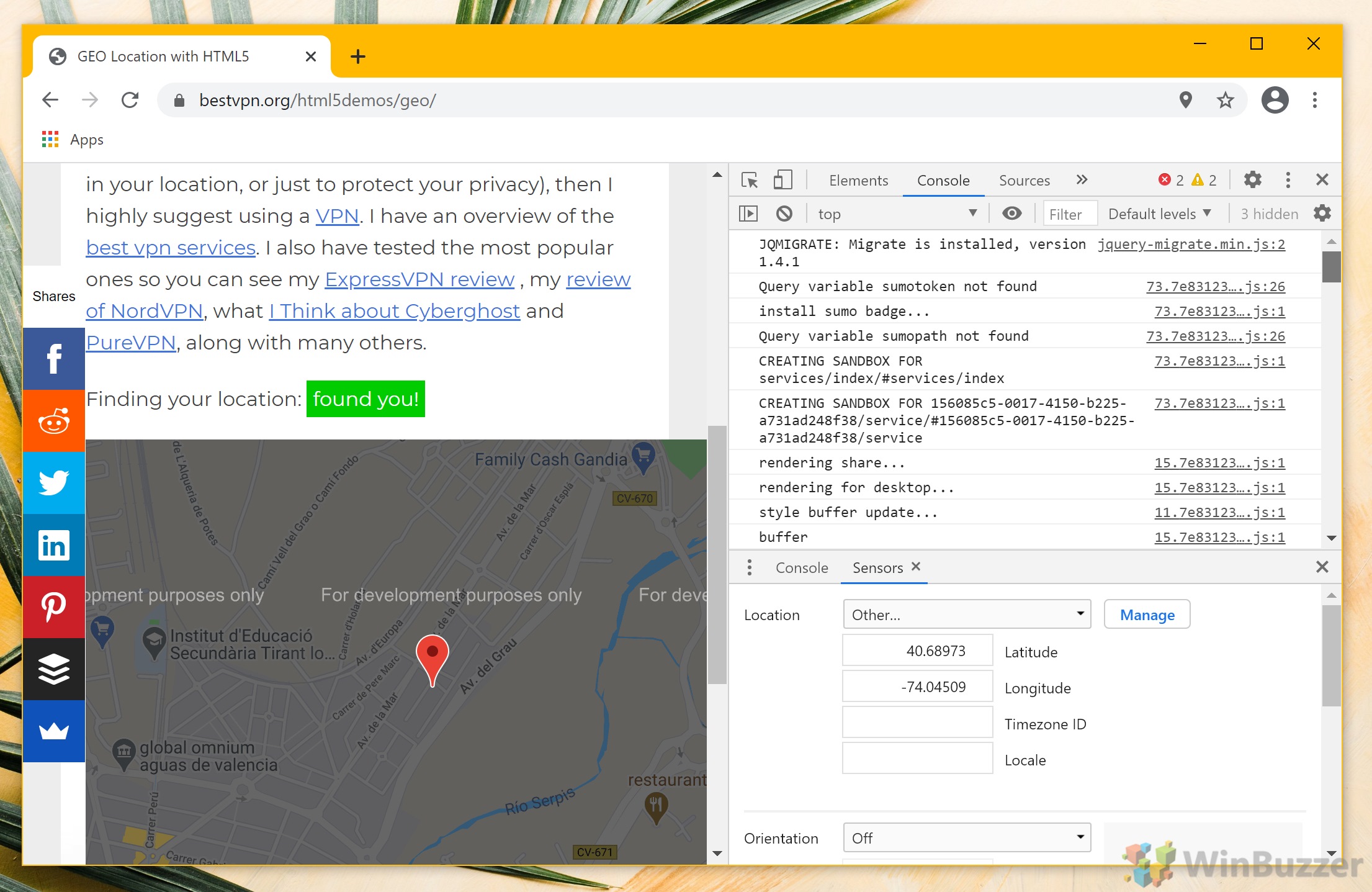
Press Ctrl + Shift + I to open Chrome’s developer panel. This is your gateway to various advanced settings, including the ability to modify your location data.

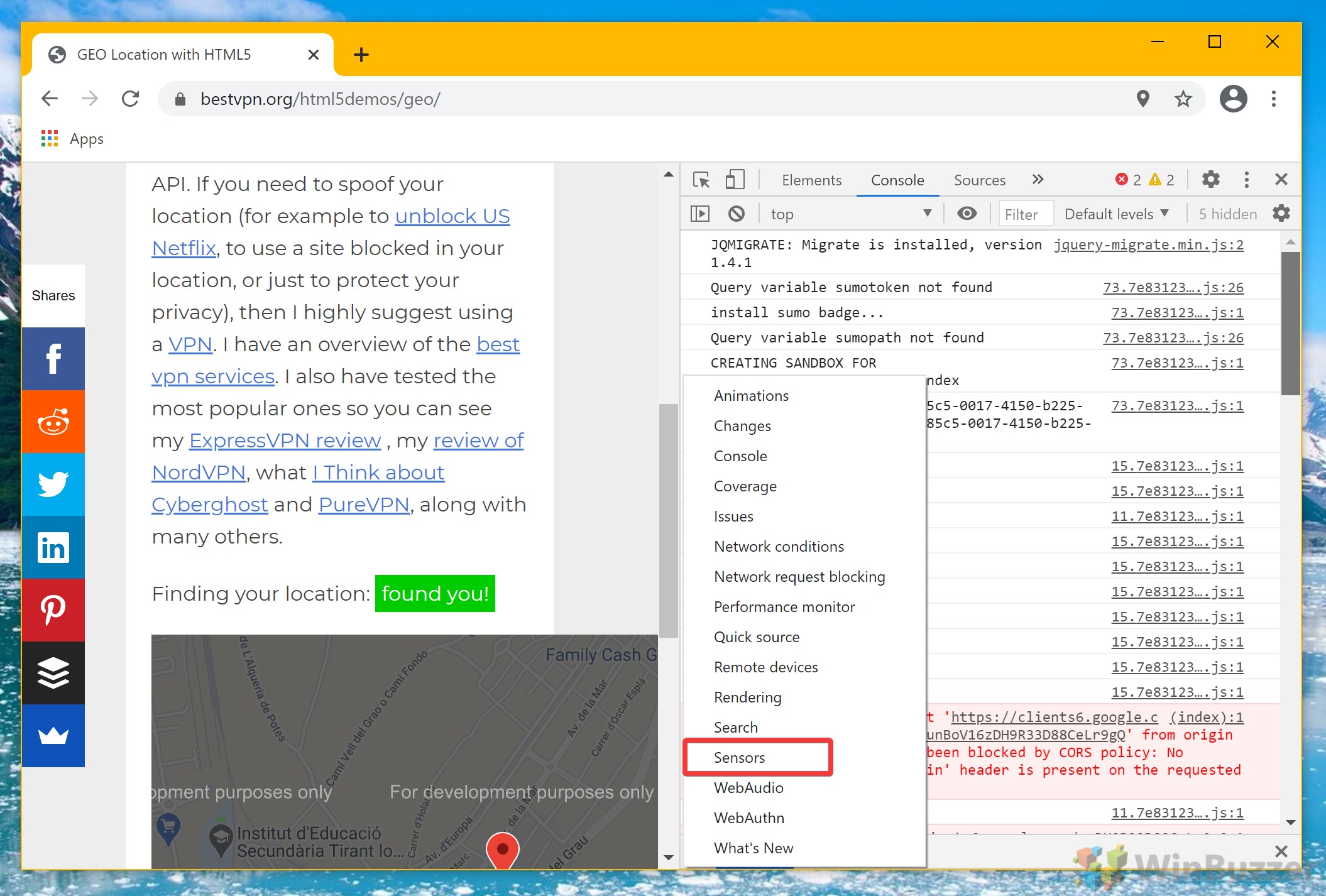
- Click ‘Sensors’
Click on the three dots next to the “Console” heading at the bottom of your screen, and select “More tools” > “Sensors“. This section allows you to modify Chrome’s geolocation data.

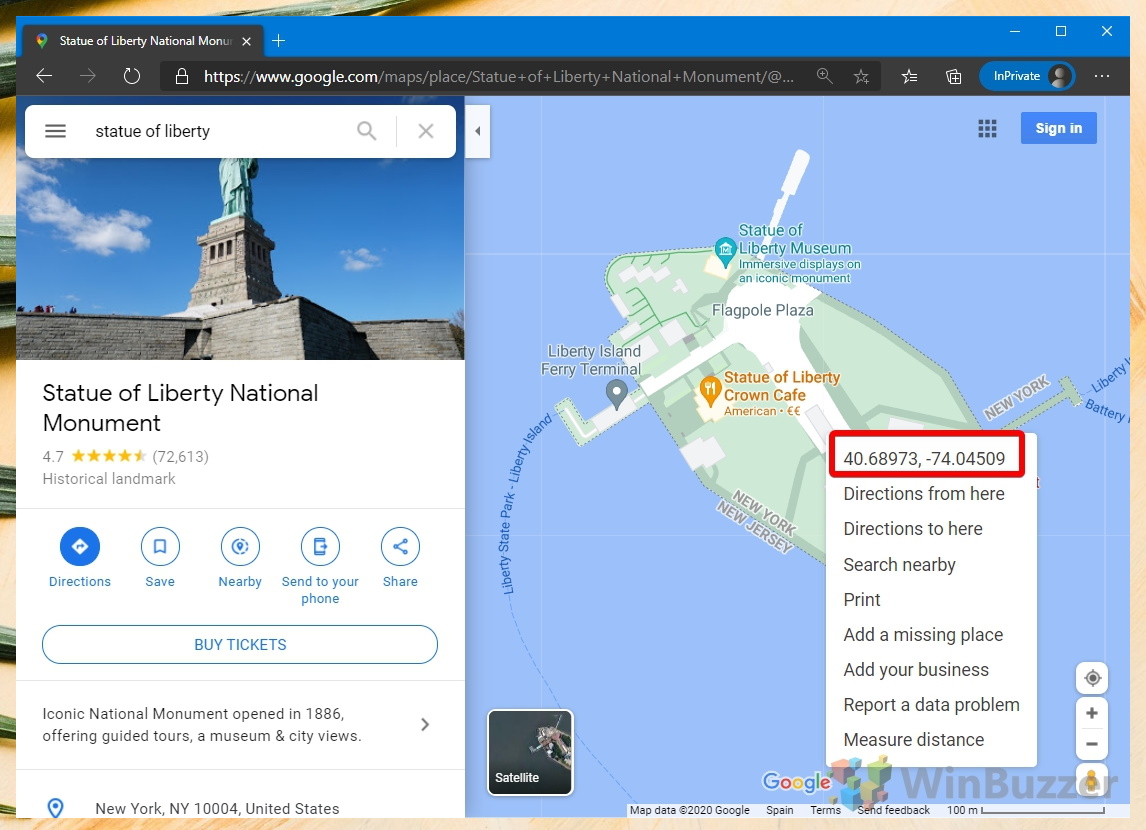
- Find your coordinates on Google Maps
Visit Google Maps, search for your desired location, then right-click on the specific point and select “What’s here?“. A box at the bottom will display the coordinates. Note these down as you’ll need them in the next steps.

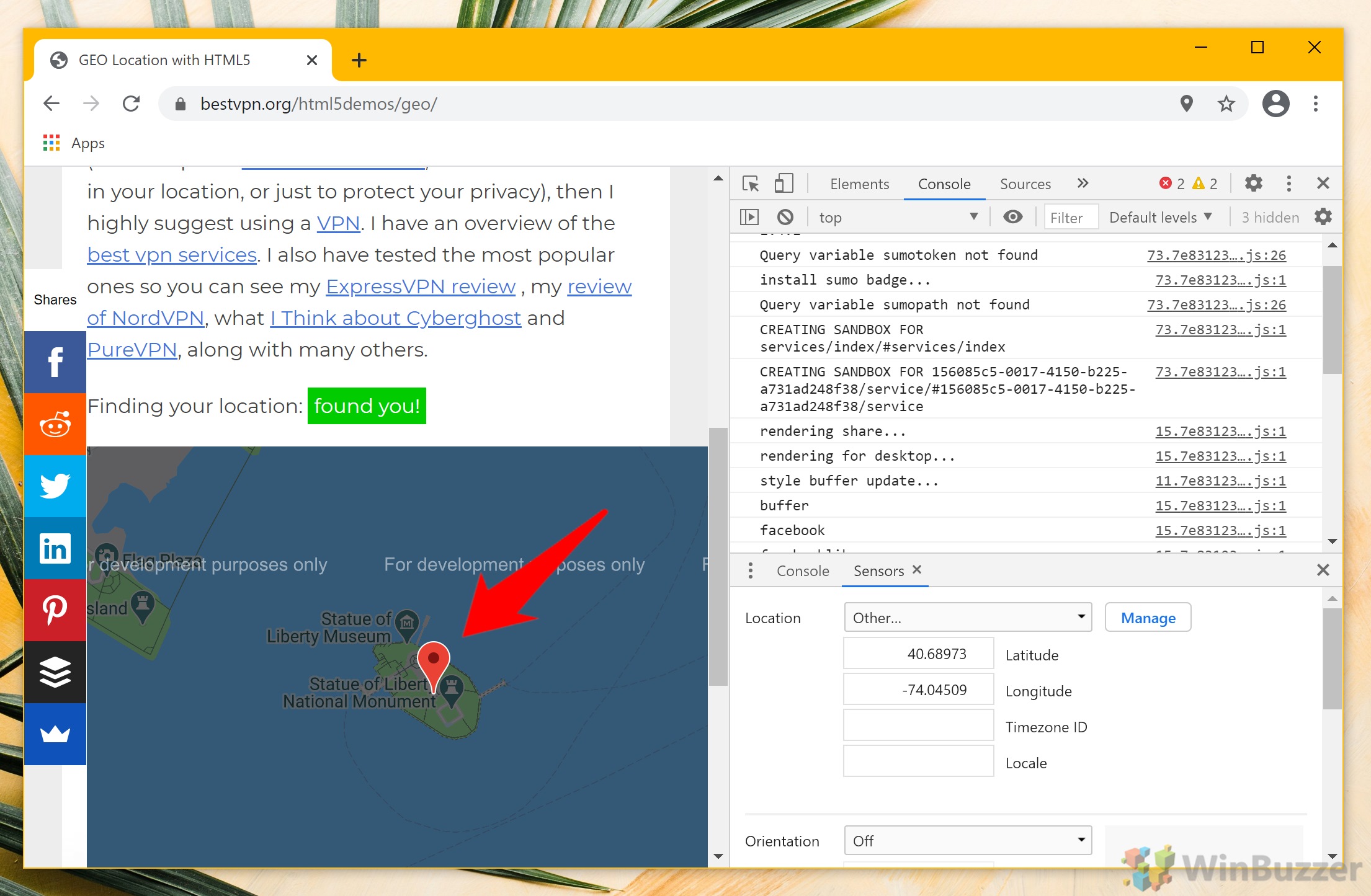
- Change geolocation via your Chrome location settings
Back in the “Sensors” tab within Chrome’s developer settings, find the “Geolocation” dropdown and select “Custom location“. Then, enter the latitude and longitude you obtained from Google Maps into the respective fields.

- Refresh the map page
After entering your new coordinates, navigate back to the webpage that uses geolocation services and refresh it. You should now see your location updated to the new coordinates you’ve set.

FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Google Chrome Location Settings
Will changing my location in Chrome affect my real IP address?
No, modifying your location in Chrome through developer settings will not change your actual IP address. Your IP address is determined by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and stays the same unless you use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or proxy. Changing your location in Chrome only alters the geographical coordinates sent to websites, not your network identity.
Can I use this method on Chrome mobile?
Unfortunately, Chrome’s mobile version does not provide access to the developer tools necessary for changing your location manually as described in the desktop version tutorial. For location spoofing on mobile devices, consider using apps designed for this purpose, but keep in mind the privacy implications and terms of service of such apps.
Is it possible to fake my location for all browsers at once?
Faking your location for all browsers simultaneously requires a system-wide location spoofing tool or software, as each browser, including Chrome, operates independently regarding geolocation settings. Look into third-party applications that can modify your entire system’s location data, but practice caution and research the security aspects of any software you install.
Can changing my location access region-locked content?
Manually changing your location in Chrome may allow access to certain region-specific content by providing websites with altered geolocation data. However, many services also analyze your IP address, which remains unchanged by this process, to accurately determine your location. For more reliable access to region-locked content, consider using a VPN service.
Does manually changing my location improve privacy?
Changing your location in Chrome can offer a temporary layer of privacy by preventing websites from accurately identifying your geographical position. However, it doesn’t conceal your IP address or browsing activity from your ISP or prevent websites from tracking you through cookies or other methods. For more robust privacy protection, use privacy-focused browsers or extensions, along with a VPN.
Will changing the location affect location-based search results?
Yes, adjusting your location settings in Chrome will impact the local search results and advertisements presented to you by search engines like Google, which use geolocation data to tailor content. For instance, searching for restaurants or weather will yield results corresponding to the manually set location rather than your real one.
Can I set a location outside my current country?
Absolutely, you can input any latitude and longitude from around the world to simulate being in a different country or region in Chrome. This feature is particularly useful for developers testing geolocation features or accessing location-specific content.
Are there limitations to how often I can change my location?
Chrome imposes no restrictions on the frequency or number of times you can change your location using the developer tools method. You can adjust your geolocation settings as often as necessary to meet your browsing preferences or requirements.
Can this location changing method be detected by websites?
Some websites implement sophisticated methods to detect inconsistencies in location data, such as mismatches between geolocation information and IP addresses, or use of known VPN addresses. While manually changing your location may work for many sites, others might still recognize your actual location or detect location spoofing.
How can I ensure my custom location is accurately applied on websites?
After entering the coordinates in Chrome’s developer settings, refresh the webpage to make sure the updated location is recognized. If a website still doesn’t register the change, double-check the coordinates for accuracy or clear your browser’s cache to prevent old location data from being used.
Do all websites request access to my location, or can some detect it automatically?
Websites require your permission to access precise location data provided by your browser. However, they can automatically approximate your location using your IP address or other data signals without explicit permission. The accuracy of this approximation varies and is generally less precise than browser-provided geolocation data.
Is there a way to temporarily disable geolocation services in Chrome without changing my location?
You can disable geolocation services entirely in Chrome’s content settings. Go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Site Settings > Location, where you can block all sites from accessing your location or decide on a site-by-site basis. This prevents websites from accessing geolocation data unless you provide explicit permission.
Can other Chrome extensions interfere with the manual location setting process?
Yes, some Chrome extensions, particularly those focused on privacy, security, or modifying web requests, can interfere with or override the manual location settings. If you encounter issues, consider disabling other extensions temporarily to identify any that may be affecting your geolocation settings.
How can I revert to my original location settings in Chrome?
To revert to your original location settings, simply clear any custom coordinates from the “Sensors” tab in Chrome’s developer settings and refresh the webpage. Chrome does not permanently store custom geolocation changes, so closing and reopening the browser also resets your location data to its default state.
Does Chrome offer any built-in tools to enhance location privacy or security?
Chrome allows users to manage which websites can access geolocation data through its site settings menu. You can choose to block all location requests, allow them, or be prompted each time a site requests access. This level of control helps enhance your privacy by ensuring only trusted sites can request and use your location data.
Related: How to Create a Custom Google Map
Google Maps is among the best tools for route finding, but sadly many of its more advanced features are tucked away. Though it’s not widely advertised, it is possible to create a custom Google map with its own pins, styles, routes, and more. Our other guide shows you how to create a custom Google map, complete with map markers, shapes, routes, and more.

Related: How to Measure Distances on Google Maps
Google Maps can measure distance in an area or as the crow flies to help you with various decisions and sate your curiosity. One good use of the tool is measure distance walked along footpaths, for example, or to determine the size of a property. In our other guide, we show you how to measure distances in Google Maps, either in an area, along a route, or as the crow flies.
Related: How to Drop a Pin in Google Maps
Renowned as one of the most helpful applications, Google Maps allows users to mark locations by “dropping a pin,” a patented inverted-drop-shaped icon that labels locations on the map. This feature is especially useful for saving addresses, marking locations without addresses, or correcting incorrect addresses. A dropped pin in Google Maps serves as a digital breadcrumb trail, guiding users through various locations and enhancing their overall mapping experience