In order to get the Windows Experience Index (WEI) score on Windows 10 or Windows 11, you will have to take a small detour.
Microsoft has banned this popular performance index from the control panel for PCs running Windows 8.1 or later. We will show you how to find that performance index anyways and help you interpreting it the right way.
What is the Windows Experience Index (WEI)?
Introduced with Windows Vista, the Windows Experience Index (WEI) shows at a glance how fast your computer is working and which hardware shortcomings it may have.
Before Windows 8.1 you were able to view the Windows Performance Index via the control panel. But even under Windows 10 or Windows 11 the Windows Experience Index is still available.
The Windows Experience Index is computed on a scale from 1.0 for the worst performance score to 9.9 for particularly high-performing computers by the so called Windows System Assessment Tool (WinSAT). As a performance index for your PC it is a practical indicator to evaluate quickly the processing power of your machine.
While being a simple numeric score as an overall grade, Windows 10 or Windows 11 calculates the WEI score based on the lowest score of four sub-ratings.
Those exist for RAM, graphic-chipset or GPU and hard disk. The Windows Experience Index thus assumes that poor performance in one sub-category slows down the computer considerably, even though performant hardware might be installed elsewhere.
While that makes really an accurate measure, the Windows Windows Experience Index might help reveal and possibly eliminate serious weaknesses of your PC. Here’s how you can get the WEI score with Windows 10 or Windows 11.
⚠️ Please note: The process described below is the same in Windows 11 as it is in Windows 10. However, bear in mind that we’ll be using screenshots from Windows 10, so your UI may look a little different. We’ll point out any changes you need to be aware of as they come up.
How to get the Windows Experience Index (WEI)
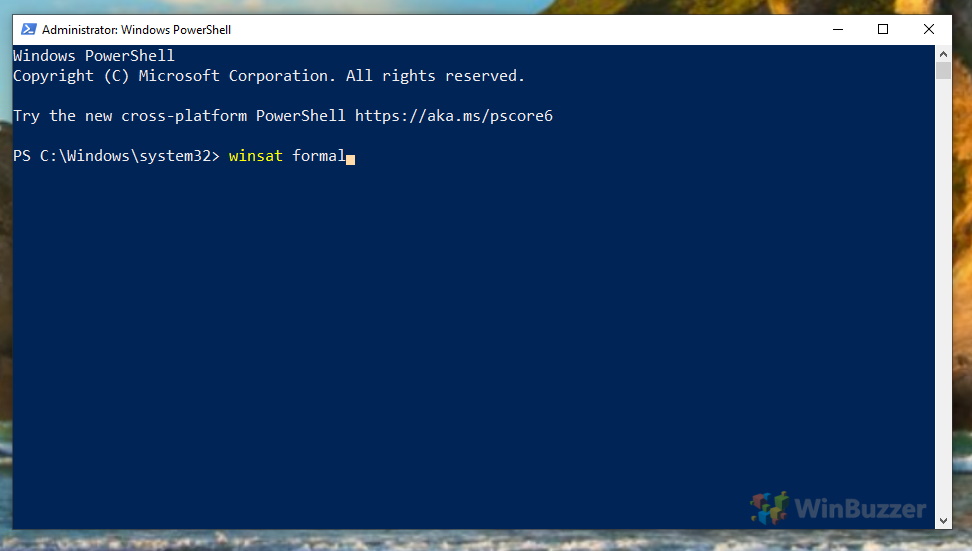
Right-click the start button to open the context menu and click on “Windows PowerShell (Admin)”.

There, run the command “winsat formal” to calculate the Windows Experience Index (WEI) score with the Windows System Assessment Tool (WinSAT). If your PowerShell-window closes automatically, just open it again as shown in the first step.
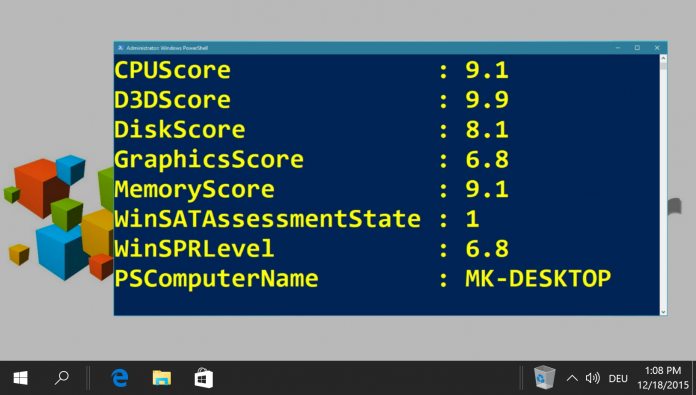
You can now display the Windows Experience Index (WEI) score using the command “Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_WinSAT”. Windows 10 will show you the following six values.
CPUScore = processor performance in calculations per second
D3DScore = 3D graphics performance
DiskScore = Data transfer rate of the primary hard disk
Graphicsscore = Graphics desktop performance for Windows (Aero)
MemoryScore = working memory (RAM) – memory operations per second
WinSPRLevel = overall rating (corresponds to the lowest partial rating)

FAQ on the Windows Experience Index (WEI)
What is a good Windows Experience Index score?
A good WEI score depends on your needs. Generally, a score above 7.0 is considered good for gaming and intensive applications, while a score around 5.0 is sufficient for general use.
How to increase the Windows Experience Index?
To increase your WEI score, upgrade hardware components like RAM, GPU, CPU, or SSD. Ensure drivers are up-to-date and unnecessary background processes are minimized.
How to read the Windows Experience Index?
The WEI score ranges from 1.0 to 9.9. It’s an overall rating based on the lowest sub-score from components like CPU, GPU, RAM, and disk performance. Higher scores indicate better performance.
What happened to the Windows Experience Index?
Microsoft removed the WEI from the Control Panel starting with Windows 8.1. However, it’s still accessible through the Windows System Assessment Tool (WinSAT) in Windows 10 and 11.
What is the Windows Experience Index rating?
The WEI rating is a numerical score reflecting the overall performance capability of your computer, based on hardware components.
What is Windows Experience Index in Windows 7?
In Windows 7, the WEI was a feature in the Control Panel that provided a performance score for the computer’s hardware.
What is the highest Windows Experience Index?
The highest possible WEI score is 9.9, indicating top-tier hardware performance.
Does a higher WEI score always mean better performance?
Generally, yes. A higher WEI score indicates better hardware performance, but real-world performance also depends on software optimization and specific use cases.
Can the WEI score change over time?
Yes, the WEI score can change if hardware is upgraded or if system performance degrades over time.
Is the WEI score relevant for gaming?
Partially. While a high WEI score indicates good hardware, gaming performance also depends on specific GPU capabilities and game optimization.
How often should I check my WEI score?
Check your WEI score after hardware upgrades or if you notice a performance decline.
Can software updates affect my WEI score?
Yes, driver updates, especially for GPU and storage, can impact your WEI score.
Is the WEI score different between Windows 10 and 11?
The method of calculating the WEI score remains the same in both Windows 10 and 11, though the user interface may differ.
Does the WEI score consider SSD performance?
Yes, the DiskScore component of the WEI reflects the data transfer rate of the primary storage, which includes SSD performance.
Can I use the WEI score to compare different computers?
Yes, the WEI score can be a useful tool for comparing the general performance of different computers, especially when considering similar hardware configurations.
Last Updated on December 31, 2023 3:36 pm CET by Markus Kasanmascheff